Serological assay for anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies improves sensitivity of diagnosis of COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 34564742
- PMCID: PMC8475848
- DOI: 10.1007/s00430-021-00721-6
Serological assay for anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies improves sensitivity of diagnosis of COVID-19 patients
Abstract
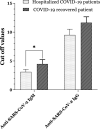
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2, responsible for coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), has become a major global health problem. The molecular testing is the accepted assay in SARS-CoV-2 detection. However, there are several reasons for low sensitivity by RNA detection, causing challenges in SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis. In this study, we aimed to investigate serological patterns of SARS-CoV-2 specific IgM, and IgG in 111 hospitalized, and 34 recovered COVID-19 patients and 311 prepandemic normal serum specimens by ELISA. The validity of the ELISA kits was evaluated using samples from normal and recovered cases. This showed that 98.1%, and 98.4% of prepandemic normal samples were negative for anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM, and IgG, respectively. Assessment of 34 COVID-19 confirmed recovered patients showed a test sensitivity of 76.5%, and 94.1% for IgM, and IgG, respectively. In COVID-19 hospitalized patients, 42.3%, and 51.4% were positive for IgM and IgG, respectively. Viral RNA was not detectable in 43.3% of the hospitalized patients. Interestingly, combined molecular and serological testing improved the sensitivity of COVID-19 diagnosis to 79.6%. Using PCR with combined IgM/IgG results augmented the patient diagnosis sensitivity to 65.3% and 87.2% in ≤ 7 days, and > 7 days intervals, respectively. Overall, serological tests in combination with PCR can improve the sensitivity of COVID-19 diagnosis.
Keywords: Antibody; COVID-19; Diagnosis; ELISA; PCR; SARS-CoV-2; Serology.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of serum IgM and IgG antibodies in COVID-19 patients by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay.J Med Virol. 2021 May;93(5):2857-2866. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26741. Epub 2021 Mar 1. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33331654
-
Evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 Capture IgM Antibody Assay in Convalescent Sera.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0045821. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00458-21. Epub 2021 Sep 8. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34494855 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of a new automated chemiluminescent anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG antibody assay system detecting both N and S proteins in Japan.PLoS One. 2021 Mar 4;16(3):e0247711. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247711. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33661990 Free PMC article.
-
Seropositivity rate and diagnostic accuracy of serological tests in 2019-nCoV cases: a pooled analysis of individual studies.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Oct;24(19):10208-10218. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202010_23243. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33090430 Review.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of serological tests and kinetics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 antibody: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Rev Med Virol. 2021 May;31(3):e2181. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2181. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Rev Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33152146
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Nucleocapsid Antibody Response in Vaccinated Croatian Healthcare Workers and Infected Hospitalized Patients: A Single Center Cohort Study.Viruses. 2022 Sep 4;14(9):1966. doi: 10.3390/v14091966. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146773 Free PMC article.
-
Immune system-related soluble mediators and COVID-19: basic mechanisms and clinical perspectives.Cell Commun Signal. 2022 Aug 29;20(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00948-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2022. PMID: 36038915 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, Liu L, Shan H, Lei CL, Hui DSC, Du B, Li LJ, Zeng G, Yuen KY, Chen RC, Tang CL, Wang T, Chen PY, Xiang J, Li SY, Wang JL, Liang ZJ, Peng YX, Wei L, Liu Y, Hu YH, Peng P, Wang JM, Liu JY, Chen Z, Li G, Zheng ZJ, Qiu SQ, Luo J, Ye CJ, Zhu SY, Zhong NS, China Medical Treatment Expert Group for C Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(18):1708–1720. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hui DS, Azhar EI, Madani TA, Ntoumi F, Kock R, Dar O, Ippolito G, Mchugh TD, Memish ZA, Drosten C. The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to global health—the latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;91:264–266. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.01.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, Qiu Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Wei Y, Xia J, Yu T, Zhang X, Zhang L. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020;395(10223):507–513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

