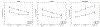A longitudinal study of the phonological organisation of novel word forms in children with developmental language disorder
- PMID: 34565237
- PMCID: PMC8976316
- DOI: 10.1080/17549507.2021.1975816
A longitudinal study of the phonological organisation of novel word forms in children with developmental language disorder
Abstract
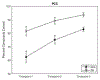
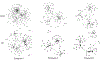
Purpose: Deficits in the production of novel words, such as in nonword repetition tasks, are one of the early hallmarks of developmental language disorder (DLD). In children with DLD, the production of novel nonwords is characterised by speech sound inaccuracy. The focus of the present study is on the stable organisation of phonological sequences. Specifically, we aimed to identify the persistence of deficits in accuracy and in variability in sound sequencing in novel word production from pre-school to the early school years.Method: Children with and without DLD produced a set of six nonwords 12 times each, initially collected when children were 4- to 5-years old. Children repeated this task over the course of two years. Analyses included phonetic accuracy as well as network science indices of sound sequence organisation.Result: Children with DLD were less accurate than their peers with typical language at each timepoint, and their productions were markedly variable, as revealed by network science metrics; these children never converged with their peers with typical language.Conclusion: The findings suggest a unique deficit in phonological sequence production that persists beyond the pre-school years. These results offer new theoretical and clinical insights into mechanisms that underlie deficits in novel word form learning.
Keywords: Developmental language disorder; sound sequencing; specific language impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- American Speech-Language-Hearing Association. (2007). Childhood Apraxia of Speech [Technical Report]. Available from www.asha.org/policy.
-
- Archibald LMD (2017). Working memory and language learning: A review. Child Language Teaching and Therapy, 33(1), 5–17. 10.1177/0265659016654206 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous