Development of a competitive chemiluminescence immunoassay using a monoclonal antibody recognizing 3B of foot-and-mouth disease virus for the rapid detection of antibodies induced by FMDV infection
- PMID: 34565393
- PMCID: PMC8474858
- DOI: 10.1186/s12985-021-01663-4
Development of a competitive chemiluminescence immunoassay using a monoclonal antibody recognizing 3B of foot-and-mouth disease virus for the rapid detection of antibodies induced by FMDV infection
Abstract
Background: Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) is a devastating animal disease. Anti-non-structural protein (NSP) antibody detection is very important for confirming suspected cases, evaluating the prevalence of infection, certifying animals for trade and controlling the disease.
Methods: In this study, a competitive chemiluminescence immunoassay (3B-cCLIA) was developed for the rapid detection of antibodies against NSPs in different species of livestock animals using the monoclonal antibody (mAb) 9E2 as a competitive antibody that recognizes NSP 3B.
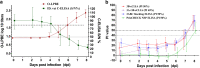
Results: The cut-off value (50%), diagnostic sensitivity (Dsn) (97.20%, 95.71%, and 96.15%) and diagnostic specificity (Dsp) (99.51%, 99.43%, and 98.36) of the assay were estimated by testing a panel of known-background sera from swine, cattle and sheep, respectively. The accuracy rate of the 3B-cCLIA was further validated and subsequently compared with that of two commercial diagnostic kits. The early diagnostic results showed that antibodies recognizing NSPs developed later (approximately 1-2 days) than antibodies recognizing structural proteins. Furthermore, anti-NSP antibody presence in animals vaccinated multiple times (false positives), especially cattle and sheep, was confirmed, and the false-positive rate increased with the number of vaccinations.
Conclusions: These results indicate that the 3B-cCLIA is suitable for the rapid detection of antibodies against FMDV NSP 3B in a wide range of species.
Keywords: Chemiluminescence immunoassay; Diagnosis; Foot-and-mouth disease virus; Monoclonal antibody; Non-structural protein.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Liu ZZ, Zhao FR, Gao SD, Shao JJ, Zhang YG, Chang HY. Development of a chemiluminescence immunoassay using recombinant non-structural epitope-based proteins to accurately differentiate foot-and-mouth disease virus-infected and vaccinated bovines. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2018;65:338–344. doi: 10.1111/tbed.12811. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu W, Shao J, Zhang G, Chang Y, Ge S, Sun Y, Gao Z, Chang H. Development of an indirect chemiluminescence immunoassay using a multiepitope recombinant protein to specifically detect antibodies against foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype O in swine. J Clin Microbiol. 2021;59:e02464–e12420. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

