A Combined Approach for Fast Nanofat Microneedling
- PMID: 34566373
- PMCID: PMC8423193
- DOI: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_142_20
A Combined Approach for Fast Nanofat Microneedling
Abstract
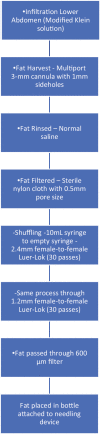
Background: Lipofilling is currently a fundamental component of rhytidoplasty and fat harvesting has become a common procedure. Tonnard introduced the concept of nanofat grafting, a revolutionary milestone, in which adipocytes are mechanically separated from the stromal vascular fraction and the latter is injected, adding the possibility of cellular therapies to the surgical field. Later, Verpaele et al. published a report using a new device to apply this nanofat in a uniform manner, which they termed nanofat needling. The device has 24 microneedles of 1.5 mm length and is applied as a stamp, in a tapping motion. The same manufacturer offers a similar model with 64 microneedles, 1.0 mm length, and available as a roller.
Objectives: We sought to evaluate the combination of the above-mentioned microneedling devices to achieve faster nanofat delivery.
Materials and methods: A prospective evaluation of patients undergoing a combined nanofat microneedling approach for skin rejuvenation and scar revision, using both a stamp device as well as a roller, was performed in a private practice setting, from January 2019 to January 2020. Patient satisfaction, complications, and surgical time were evaluated.
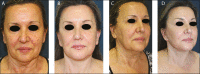
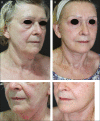
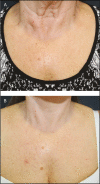
Results: We applied this combination treatment to over 100 treatment areas in 86 patients over a 12-month period, with a short operative time, no increase in complications, consistent results, and good patient satisfaction.
Conclusions: We recommend the use of this new device in association with the original one, in order to decrease the procedure time. We designate this strategy "fast nanofat microneedling."
Keywords: Collagen induction; facial rejuvenation; fat grafting; microneedling; nanofat.
Copyright: © 2021 Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Tonnard P, Verpaele A, Peeters G, Hamdi M, Cornelissen M, Declercq H. Nanofat grafting: Basic research and clinical applications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013;132:1017–26. - PubMed
-
- Verpaele A, Tonnard P, Jeganathan C, Ramaut L. Nanofat needling: A novel method for uniform delivery of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction into the skin. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;143:1062–5. - PubMed
-
- Tonnard P, Verpaele A, Carvas M. Fat grafting for facial rejuvenation with nanofat grafts. Clin Plast Surg. 2020;47:53–62. - PubMed
-
- Alster TS, Graham PM. Microneedling: A review and practical guide. Dermatol Surg. 2018;44:397–404. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
