Generic sensor platform based on electro-responsive molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles (e-NanoMIPs)
- PMID: 34567693
- PMCID: PMC8433225
- DOI: 10.1038/s41378-020-00193-3
Generic sensor platform based on electro-responsive molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles (e-NanoMIPs)
Abstract
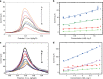
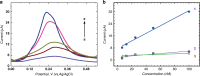
The present research describes the design of robust electrochemical sensors based on electro-responsive molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles (e-MIPs). The e-MIPs, tagged with a redox probe, combine both recognition and reporting functions. This system replaces enzyme-mediator pairs used in traditional biosensors. The analyte recognition process relies on the generic actuation phenomenon when the polymer conformation of e-MIPs is changing in response to the presence of the template analyte. The analyte concentration is measured using voltammetric methods. In an exemplification of this technology, electrochemical sensors were developed for the determination of concentrations of trypsin, glucose, paracetamol, C4-homoserine lactone, and THC. The present technology allows for the possibility of producing generic, inexpensive, and robust disposable sensors for clinical, environmental, and forensic applications.
Keywords: Bionanoelectronics; Nanoparticles.
© The Author(s) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ugalmugale, S., Swain, R. & (Global Market insights Inc., 2018).
-
- Sadana, A., Sadana, N. & Sadana, R. A Fractal Analysis of Chemical Kinetics with Applications to Biological and Biosensor Interfaces. 1st ed., p. 337 (Elsevier Science, 2018).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
