VGEA: an RNA viral assembly toolkit
- PMID: 34567846
- PMCID: PMC8428259
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12129
VGEA: an RNA viral assembly toolkit
Abstract
Next generation sequencing (NGS)-based studies have vastly increased our understanding of viral diversity. Viral sequence data obtained from NGS experiments are a rich source of information, these data can be used to study their epidemiology, evolution, transmission patterns, and can also inform drug and vaccine design. Viral genomes, however, represent a great challenge to bioinformatics due to their high mutation rate and forming quasispecies in the same infected host, bringing about the need to implement advanced bioinformatics tools to assemble consensus genomes well-representative of the viral population circulating in individual patients. Many tools have been developed to preprocess sequencing reads, carry-out de novo or reference-assisted assembly of viral genomes and assess the quality of the genomes obtained. Most of these tools however exist as standalone workflows and usually require huge computational resources. Here we present (Viral Genomes Easily Analyzed), a Snakemake workflow for analyzing RNA viral genomes. VGEA enables users to map sequencing reads to the human genome to remove human contaminants, split bam files into forward and reverse reads, carry out de novo assembly of forward and reverse reads to generate contigs, pre-process reads for quality and contamination, map reads to a reference tailored to the sample using corrected contigs supplemented by the user's choice of reference sequences and evaluate/compare genome assemblies. We designed a project with the aim of creating a flexible, easy-to-use and all-in-one pipeline from existing/stand-alone bioinformatics tools for viral genome analysis that can be deployed on a personal computer. VGEA was built on the Snakemake workflow management system and utilizes existing tools for each step: fastp (Chen et al., 2018) for read trimming and read-level quality control, BWA (Li & Durbin, 2009) for mapping sequencing reads to the human reference genome, SAMtools (Li et al., 2009) for extracting unmapped reads and also for splitting bam files into fastq files, IVA (Hunt et al., 2015) for de novo assembly to generate contigs, shiver (Wymant et al., 2018) to pre-process reads for quality and contamination, then map to a reference tailored to the sample using corrected contigs supplemented with the user's choice of existing reference sequences, SeqKit (Shen et al., 2016) for cleaning shiver assembly for QUAST, QUAST (Gurevich et al., 2013) to evaluate/assess the quality of genome assemblies and MultiQC (Ewels et al., 2016) for aggregation of the results from fastp, BWA and QUAST. Our pipeline was successfully tested and validated with SARS-CoV-2 (n = 20), HIV-1 (n = 20) and Lassa Virus (n = 20) datasets all of which have been made publicly available. VGEA is freely available on GitHub at: https://github.com/pauloluniyi/VGEA under the GNU General Public License.
Keywords: Assembly; Genome; NGS; VGEA.
©2021 Oluniyi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Simon D.W. Frost is employed by Microsoft Research and is an Academic Editor for PeerJ. All other authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
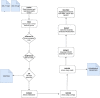

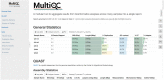
References
-
- Ajogbasile FV, Oguzie JU, Oluniyi PE, Eromon PE, Uwanibe JN, Mehta SB, Siddle KJ, Odia I, Winnicki SM, Akpede N, Akpede G, Okogbenin S, Ogbaini-Emovon E, MacInnis BL, Folarin OA, Modjarrad K, Schaffner SF, Tomori O, Ihekweazu C, Sabeti PC, Happi CT. Real-time metagenomic analysis of undiagnosed fever cases unveils a yellow fever outbreak in edo state, Nigeria. Scientific Reports. 2020;10:3180. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59880-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van der Auwera GA, Carneiro MO, Hartl C, Poplin R, Del Angel G, Levy-Moonshine A, Jordan T, Shakir K, Roazen D, Thibault J, Banks E, Garimella KV, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, De Pristo MA. From FastQ data to high confidence variant calls: the Genome Analysis Toolkit best practices pipeline. Current Protocols in Bioinformatics. 2013;43(1110):11.10.1–11.10.33. doi: 10.1002/0471250953.bi1110s43. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. Journal of Computational Biology: A Journal of Computational Molecular Cell Biology. 2012;19:455–477. doi: 10.1089/cmb.2012.0021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

