Successful treatment of cervical and upper thoracic esophageal adenocarcinoma using induction chemotherapy followed by surgery: a case report
- PMID: 34567948
- PMCID: PMC8421492
- DOI: 10.1007/s13691-021-00505-y
Successful treatment of cervical and upper thoracic esophageal adenocarcinoma using induction chemotherapy followed by surgery: a case report
Abstract
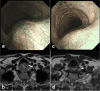
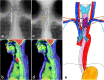
Cervical esophageal adenocarcinoma has a low incidence rate and its treatment involves various strategies. We report a patient with locally advanced cervical to upper esophageal adenocarcinoma who was able to undergo induction chemotherapy and radical surgery. A 55-year-old man was diagnosed with a poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma between the cervical and upper thoracic esophagus. The primary lesion had infiltrated into the tracheal membrane and had metastasized into the cervical lymph nodes. The initial diagnosis was T4bN1M1 stage IVB. The lower edge of the tumor was close to the tracheal bifurcation, making it difficult to create a longitudinal tracheal foramen during surgery. Therefore, when biweekly-DCF therapy was performed as induction chemotherapy, the tumor shrank sufficiently and its infiltration into the tracheal membrane decreased subsequently. We performed total laryngopharyngoesophagectomy with three-field lymph node dissection and reconstruction using free jejunal grafts and subtotal stomach via a posterior mediastinum route and a permanent tracheal foramen as a radical surgery. The pathological diagnosis was T2/MP, N1, and the effect of chemotherapy was grade 2. Cervical esophageal adenocarcinoma was rare, but technically reliable and safe oncologic surgery was possible after induction chemotherapy.
Keywords: Cervical esophageal adenocarcinoma; Induction chemotherapy; Total laryngopharyngoesophagectomy.
© The Japan Society of Clinical Oncology 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestDr. Yoshida reports receipt of grants, personal fees and non-financial support from EA Pharma Co., Ltd., Sanofi, Yakult Honsha Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Merck Serono Co., Ltd., and Novartis Pharma K.K.; and grants from Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd. outside of the submitted work. Other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Yamaji T, Tsugane S. Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. In: Ando N, editor. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Singapore: Springer; 2020. pp. 1–13.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
