Dexmedetomidine Relieves Neuropathic Pain in Rats With Chronic Constriction Injury via the Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway
- PMID: 34568327
- PMCID: PMC8455886
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.714996
Dexmedetomidine Relieves Neuropathic Pain in Rats With Chronic Constriction Injury via the Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway
Abstract
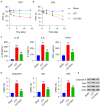
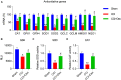
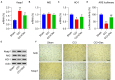
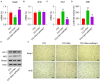
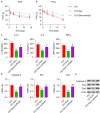
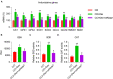
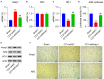
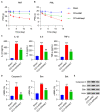
This study aimed to determine the role of dexmedetomidine (Dex) in neuropathic pain (NP) after chronic constriction injury (CCI) in a rat model as well as its underlying mechanism. First, a CCI rat model was established. After treatment with Dex, the severity of NP was ascertained by monitoring paw withdrawal threshold (PWT) and paw withdrawal latency (PWL) at different time points. Immunohistochemical analysis was performed to determine the levels of Keap1 and Nrf2 in the spinal cord. Furthermore, the levels of Keap1-Nrf2-HO-1 pathway molecules, apoptotic proteins, and antioxidant genes in the spinal cord or isolated primary microglia were determined using quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. The release of proinflammatory cytokines was detected via enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. To evaluate Dex-treated CCI-induced NP via the Keap1-Nrf2-HO-1 pathway, the rats were intrathecally injected with lentivirus to upregulate or downregulate the expression of Keap1. We found that Dex inhibited pathological changes and alleviated sciatic nerve pain as well as repressed inflammation, apoptosis, and redox disorders of the spinal cord in CCI rats. Keap1 protein expression was substantially downregulated, whereas Nrf2 and HO-1 expressions were significantly upregulated in the spinal cord after Dex administration. Additionally, Keap1 overexpression counteracted Dex-mediated inhibition of NP. Keap1 overexpression led to a decrease in Nrf2 and HO-1 levels as well as PWT and PWL but led to an aggravation of inflammation and antioxidant disorders and increased apoptosis. Keap1 silencing alleviated NP in rats with CCI, as evidenced by an increase in PWT and PWL. Keap1 depletion resulted in the alleviation of inflammation and spinal cord tissue injury in CCI rats. Collectively, these findings suggest that Dex inhibits the Keap1-Nrf2-HO-1-related antioxidant response, inflammation, and apoptosis, thereby alleviating NP in CCI rats.
Keywords: apoptosis; chronic constriction injury; inflammation; neuropathic pain; pain behavior; redox equilibrium.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Liu, Wang, Wan, Liu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MG53 ameliorates nerve injury induced neuropathic pain through the regulation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in rats.Behav Brain Res. 2023 Jul 9;449:114489. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114489. Epub 2023 May 9. Behav Brain Res. 2023. PMID: 37169128
-
Dexmedetomidine alleviates inflammation in neuropathic pain by suppressing NLRP3 via Nrf2 activation.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Oct;22(4):1046. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10479. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34434260 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 mediates the antinociceptive activity of dexmedetomidine in an acute inflammatory visceral pain rat model by activating the NF-κB sensor.Cell Biochem Funct. 2020 Jan;38(1):97-105. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3456. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020. PMID: 31773760
-
LncRNA FTX ameliorates neuropathic pain by targeting miR-320a in a rat model of chronic constriction injury.Folia Neuropathol. 2023;61(3):291-300. doi: 10.5114/fn.2023.126846. Folia Neuropathol. 2023. PMID: 37818689
-
MicroRNA-340-5p relieved chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain by targeting Rap1A in rat model.Genes Genomics. 2019 Jun;41(6):713-721. doi: 10.1007/s13258-019-00802-0. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Genes Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30848438
Cited by
-
The Effects of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2 (NFE2)-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2) Activation in Preclinical Models of Peripheral Neuropathic Pain.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Feb 21;11(2):430. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020430. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress on the Mechanisms and Neuroprotective Benefits of Dexmedetomidine in Brain Diseases.Brain Behav. 2024 Nov;14(11):e70116. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70116. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 39482839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuin 3 is required for the dexmedetomidine-mediated alleviation of inflammation and oxidative stress in nephritis.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Jan;12(1):e1135. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1135. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 38270316 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine attenuates airway inflammation and oxidative stress in asthma via the Nrf2 signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Jan;27(1):2. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12889. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 36321783 Free PMC article.
-
The Antinociceptive Role of Nrf2 in Neuropathic Pain: From Mechanisms to Clinical Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 15;16(8):1068. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081068. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204413 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

