The transmission modes and sources of COVID-19: A systematic review
- PMID: 34568614
- PMCID: PMC7484735
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijso.2020.08.017
The transmission modes and sources of COVID-19: A systematic review
Abstract
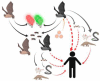
The current rampant coronavirus infection in humans, commonly known as COVID-19, a pandemic that may cause mortality in humans, has been declared a global emergency by the World Health Organization (WHO). The morbidity and mortality rates due to the pandemic are increasing rapidly worldwide, with the USA most affected by the disease. The source COVID-19 is not absolutely clear; however, the disease may be transmitted by either by COVID-19-positive individuals or from a contaminated environment. In this review, we focused on how the COVID-19 virus is transmitted in the community. An extensive literature search was conducted using specific keywords and criteria. Based on the published report, it is concluded that COVID-19 is primarily transmitted human-to-human via oral and respiratory aerosols and droplets with the virus-contaminated environment play a lesser role in the propagation of disease. Healthcare providers and the elderly with comorbidities are especially susceptible to the infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; Pandemic infection; Transmission mode; Virus load and shedding; Virus source.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC)-2019 . 2020. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV)2020 Feb 1.
-
- Olivencia G.R., Membrillo de Novales F.J., Rosado M.V.G., Figueras A.I.L., Alonso P.C., Estébanez M. 2020. Quarantine for SARS-CoV-2 in Spain: how did we do it?
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) situation report. 2020;9(29)
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources