Single-step genomic BLUP enables joint analysis of disconnected breeding programs: an example with Eucalyptus globulus Labill
- PMID: 34568915
- PMCID: PMC8473980
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab253
Single-step genomic BLUP enables joint analysis of disconnected breeding programs: an example with Eucalyptus globulus Labill
Abstract
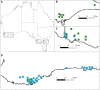
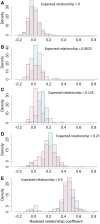
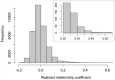
Single-step GBLUP (HBLUP) efficiently combines genomic, pedigree, and phenotypic information for holistic genetic analyses of disjunct breeding populations. We combined data from two independent multigenerational Eucalyptus globulus breeding populations to provide direct comparisons across the programs and indirect predictions in environments where pedigreed families had not been evaluated. Despite few known pedigree connections between the programs, genomic relationships provided the connectivity required to create a unified relationship matrix, H, which was used to compare pedigree-based and HBLUP models. Stem volume data from 48 sites spread across three regions of southern Australia and wood quality data across 20 sites provided comparisons of model accuracy. Genotyping proved valuable for correcting pedigree errors and HBLUP more precisely defines relationships within and among populations, with relationships among the genotyped individuals used to connect the pedigrees of the two programs. Cryptic relationships among the native range populations provided evidence of population structure and evidence of the origin of landrace populations. HBLUP across programs improved the prediction accuracy of parents and genotyped individuals and enabled breeding value predictions to be directly compared and inferred in regions where little to no testing has been undertaken. The impact of incorporating genetic groups in the estimation of H will further align traditional genetic evaluation pipelines with approaches that incorporate marker-derived relationships into prediction models.
Keywords: HBLUP; MPP; Multiparental Populations; Myrtaceae; breeding value accuracy; forest tree breeding; genomic relationship matrix; genomic selection.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Aguilar I, Misztal I, Johnson DL, Legarra A, Tsuruta S, et al.2010. A unified approach to utilize phenotypic, full pedigree, and genomic information for genetic evaluation of Holstein final score. J Dairy Sci. 93:743–752. - PubMed
-
- Aguilar I, Misztal I, Tsuruta S, Legarra A, Wang H.. 2014. PREGSF90 - POSTGSF90: computational tools for the implementation of single-step genomic selection and genome-wide association with ungenotyped individuals in BLUPF90 programs. 10. World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production (WCGALP), Aug 2014, Vancouver, Canada. American Society of Animal Science, 2014, Proceedings 10th Congress of Genetics Applied to Livestock Production.
-
- Araujo JA, Borralho NMG, Dehon G.. 2012. The importance and type of non-additive genetic effects for growth in Eucalyptus globulus. Tree Genet Genom. 8:327–337.
-
- Baltunis BS, Wu HX, Dungey HS, Mullin TJ, Brawner JT.. 2009. Comparisons of genetic parameters and clonal value predictions from clonal trials and seedling base population trials of radiata pine. Tree Genet Genom. 5:269–278.
-
- Borralho NMG. 1995. The impact of individual tree mixed models (BLUP) in tree breeding strategies. In: Eucalypt Plantations: Improving Fibre Yield and Quality. Proceedings of the CRCTHF-IUFRO Conference, Hobart, Australia, 19-24 February 1995. Cooperative Research Centre for Temperate Hardwood Forestry: p. 141–145.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
