Characterization of the β-tubulin gene family in Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum and its implication for the molecular detection of benzimidazole resistance
- PMID: 34570778
- PMCID: PMC8496844
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009777
Characterization of the β-tubulin gene family in Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum and its implication for the molecular detection of benzimidazole resistance
Abstract
Background: The treatment coverage of control programs providing benzimidazole (BZ) drugs to eliminate the morbidity caused by soil-transmitted helminths (STHs) is unprecedently high. This high drug pressure may result in the development of BZ resistance in STHs and so there is an urgent need for surveillance systems detecting molecular markers associated with BZ resistance. A critical prerequisite to develop such systems is an understanding of the gene family encoding β-tubulin proteins, the principal targets of BZ drugs.
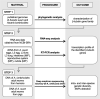
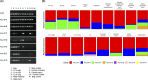
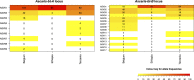
Methodology and principal findings: First, the β-tubulin gene families of Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum were characterized through the analysis of published genomes. Second, RNA-seq and RT-PCR analyses on cDNA were applied to determine the transcription profiles of the different gene family members. The results revealed that Ascaris species have at least seven different β-tubulin genes of which two are highly expressed during the entire lifecycle. Third, deep amplicon sequencing was performed on these two genes in more than 200 adult A. lumbricoides (Ethiopia and Tanzania) and A. suum (Belgium) worms, to investigate the intra- and inter-species genetic diversity and the presence of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) that are associated with BZ resistance in other helminth species; F167Y (TTC>TAC or TTT>TAT), E198A (GAA>GCA or GAG>GCG), E198L (GAA>TTA) and F200Y (TTC>TAC or TTT>TAT). These particular SNPs were absent in the two investigated genes in all three Ascaris populations.
Significance: This study demonstrated the presence of at least seven β-tubulin genes in Ascaris worms. A new nomenclature was proposed and prioritization of genes for future BZ resistance research was discussed. This is the first comprehensive description of the β-tubulin gene family in Ascaris and provides a framework to investigate the prevalence and potential role of β-tubulin sequence polymorphisms in BZ resistance in a more systematic manner than previously possible.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of key interactions of benzimidazole resistance-associated amino acid mutations in Ascaris β-tubulins by molecular docking simulations.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 12;12(1):13725. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16765-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35961997 Free PMC article.
-
Assays to detect beta-tubulin codon 200 polymorphism in Trichuris trichiura and Ascaris lumbricoides.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009;3(3):e397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000397. Epub 2009 Mar 24. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2009. PMID: 19308251 Free PMC article.
-
First identification of the benzimidazole resistance-associated F200Y SNP in the beta-tubulin gene in Ascaris lumbricoides.PLoS One. 2019 Oct 17;14(10):e0224108. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224108. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31622428 Free PMC article.
-
Are Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum a single species?Parasit Vectors. 2012 Feb 20;5:42. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-5-42. Parasit Vectors. 2012. PMID: 22348306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Comparative studies on the difference between Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum].Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2006 Apr 30;24(2):140-3, 145. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16862915 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Anthelmintic resistance in soil-transmitted helminths: One-Health considerations.Parasitol Res. 2023 Dec 20;123(1):62. doi: 10.1007/s00436-023-08088-8. Parasitol Res. 2023. PMID: 38114766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of key interactions of benzimidazole resistance-associated amino acid mutations in Ascaris β-tubulins by molecular docking simulations.Sci Rep. 2022 Aug 12;12(1):13725. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16765-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35961997 Free PMC article.
-
Deep-amplicon sequencing of the complete beta-tubulin gene in Trichuris trichiura before and after albendazole treatment.Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2024 Dec;26:100570. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2024.100570. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39546832 Free PMC article.
-
Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with benzimidazole resistance of the β-tubulin isotype 1 gene in Ascaris lumbricoides isolated in South Africa.Braz J Infect Dis. 2025 Jun 28;29(5):104556. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2025.104556. Online ahead of print. Braz J Infect Dis. 2025. PMID: 40582181 Free PMC article.
-
Worms and bugs of the gut: the search for diagnostic signatures using barcoding, and metagenomics-metabolomics.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Apr 1;15(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05225-7. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 35365192 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminthiases: numbers of people treated in 2019. Weekly Epidemiological Record. 2020;95(50):629–40.
-
- World Health Organization. Soil-transmitted helminthiases: number of children treated in 2010. Weekly Epidemiological Record. 2012;87(23):225–32. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (2020). 2030 targets for soil-transmitted helminthiases control programmes. World Health Organization, Geneva.
-
- Vercruysse J, Albonico M, Behnke JM, Kotze AC, Prichard RK, McCarthy JS, et al.. Is anthelmintic resistance a concern for the control of human soil-transmitted helminths? International Journal for Parasitology: Drugs and Drug Resistance. 2011;1(1):14–27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpddr.2011.09.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

