Behaviour and animal welfare indicators of broiler chickens housed in an enriched environment
- PMID: 34570782
- PMCID: PMC8476007
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256963
Behaviour and animal welfare indicators of broiler chickens housed in an enriched environment
Abstract
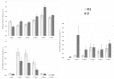
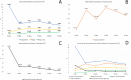
The present study aimed to assess the influence of adding straw bales, step platforms, and laser projectors as environmental enrichment resources on the behaviour and welfare indicators of broiler chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus). A sample of 4,000 day-old male Cobb® 500 birds was used. The experimental treatments consisted of No Environmental Enrichment (NEE)-similar to a conventional environment; and Environmental Enrichment (EE)-environment enriched with straw bales, step platforms, and laser projectors, with four replicates per treatment of 500 animals. Behavioural characteristics (ethological observation through cameras, grab test, and modified touch test) and animal welfare indicators (pododermatitis and dorsal cranial myopathy) were assessed. The birds submitted to the EE treatment exhibited greater exploratory activity and expression of behaviours associated with comfort and welfare, whereas those in the NEE group were less active. Locomotion and play fighting behaviour decreased and behaviours associated with comfort increased as age advanced. The frequencies of interaction with laser spots and birds lying around straw bales were the highest in the 1st week (P<0.01). The behaviours of pecking at straw bales (P<0.0004), using the step platforms (P = 0.0001) and being on top of straw bales (P<0.0002) gradually increased. The chickens accessed the feeding troughs the most in the period of 0800 hours (P<0.0001) and expressed the highest frequencies of behaviours associated with comfort in the 1400 hours and 1700 hours periods. The birds in the EE group were calmer in face of human presence and touch and scored higher in animal welfare indicators. Adding straw bales, step platforms, and laser projectors increased locomotion, reduced expression of fear, and improved animal welfare indicators of broiler chickens.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Costa L, Pereira D, Bueno L, Pandorfi H. Some aspects of chicken behavior and welfare. Brazilian J Poult Sci. 2012;14: 159–164. doi: 10.1590/S1516-635X2012000300001 - DOI
-
- Tahamtani FM, Pedersen IJ, Toinon C, Riber AB. Effects of environmental complexity on fearfulness and learning ability in fast growing broiler chickens. Appl Anim Behav Sci. 2018;207: 49–56. doi: 10.1016/j.applanim.2018.04.005 - DOI
-
- Welfare Quality ®. Welfare Quality® assessment protocol for poultry (broilers, laying hens). Welfare Quality® Consortium, Lelystad, Netherlands. 2009. doi: 10.5433/1679-0359.2013v34n6Supl2p4213 - DOI
-
- Garcia RG, Almeida Paz ICL, Caldara FR, Nääs IA, Pereira DF, Ferreira VMOS. Selecting the most adequate bedding material for broiler production in Brazil. Brazilian J Poult Sci. 2012;14: 121–127. doi: 10.1590/S1516-635X2012000200006 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

