The megakaryocytic transcription factor ARID3A suppresses leukemia pathogenesis
- PMID: 34570885
- PMCID: PMC9632760
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2021012231
The megakaryocytic transcription factor ARID3A suppresses leukemia pathogenesis
Abstract
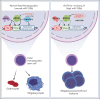
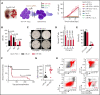
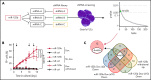
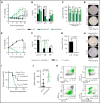
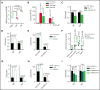
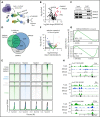
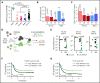
Given the plasticity of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells, multiple routes of differentiation must be blocked in the the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia, the molecular basis of which is incompletely understood. We report that posttranscriptional repression of the transcription factor ARID3A by miR-125b is a key event in the pathogenesis of acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL). AMKL is frequently associated with trisomy 21 and GATA1 mutations (GATA1s), and children with Down syndrome are at a high risk of developing the disease. The results of our study showed that chromosome 21-encoded miR-125b synergizes with Gata1s to drive leukemogenesis in this context. Leveraging forward and reverse genetics, we uncovered Arid3a as the main miR-125b target behind this synergy. We demonstrated that, during normal hematopoiesis, this transcription factor promotes megakaryocytic differentiation in concert with GATA1 and mediates TGFβ-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in complex with SMAD2/3. Although Gata1s mutations perturb erythroid differentiation and induce hyperproliferation of megakaryocytic progenitors, intact ARID3A expression assures their megakaryocytic differentiation and growth restriction. Upon knockdown, these tumor suppressive functions are revoked, causing a blockade of dual megakaryocytic/erythroid differentiation and subsequently of AMKL. Inversely, restoring ARID3A expression relieves the arrest of megakaryocytic differentiation in AMKL patient-derived xenografts. This work illustrates how mutations in lineage-determining transcription factors and perturbation of posttranscriptional gene regulation can interact to block multiple routes of hematopoietic differentiation and cause leukemia. In AMKL, surmounting this differentiation blockade through restoration of the tumor suppressor ARID3A represents a promising strategy for treating this lethal pediatric disease.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Posttranscriptional Arid3a deregulation in AMKL.Blood. 2022 Feb 3;139(5):637-638. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021014081. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35113150 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sanz MA, Grimwade D, Tallman MS, et al. . Management of acute promyelocytic leukemia: recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood. 2009;113(9): 1875-1891. - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Godinho FJ, Klusmann JH, Garriga-Canut M, Yu C, Orkin SH. Developmental stage-selective effect of somatically mutated leukemogenic transcription factor GATA1. Nat Genet. 2005;37(6):613-619. - PubMed
-
- Wechsler J, Greene M, McDevitt MA, et al. . Acquired mutations in GATA1 in the megakaryoblastic leukemia of Down syndrome. Nat Genet. 2002;32(1):148-152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

