Randomised clinical trial: semaglutide versus placebo reduced liver steatosis but not liver stiffness in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease assessed by magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 34570916
- PMCID: PMC9292692
- DOI: 10.1111/apt.16608
Randomised clinical trial: semaglutide versus placebo reduced liver steatosis but not liver stiffness in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease assessed by magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists may be a treatment option in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Aims: To investigate the effects of semaglutide on liver stiffness and liver fat in subjects with NAFLD using non-invasive magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) methods.
Methods: This randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial enrolled subjects with liver stiffness 2.50-4.63 kPa by magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) and liver steatosis ≥10% by MRI proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF). The primary endpoint was change from baseline to week 48 in liver stiffness assessed by MRE.
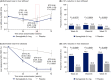
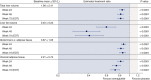
Results: Sixty-seven subjects were randomised to once-daily subcutaneous semaglutide 0.4 mg (n = 34) or placebo (n = 33). Change from baseline in liver stiffness was not significantly different between semaglutide and placebo at week 48 (estimated treatment ratio 0.96 (95% CI 0.89, 1.03; P = 0.2798); significant differences in liver stiffness were not observed at weeks 24 or 72. Reductions in liver steatosis were significantly greater with semaglutide (estimated treatment ratios: 0.70 [0.59, 0.84], P = 0.0002; 0.47 [0.36, 0.60], P < 0.0001; and 0.50 [0.39, 0.66], P < 0.0001) and more subjects achieved a ≥ 30% reduction in liver fat content with semaglutide at weeks 24, 48 and 72, (all P < 0.001). Decreases in liver enzymes, body weight and HbA1c were also observed with semaglutide.
Conclusions: The change in liver stiffness in subjects with NAFLD was not significantly different between semaglutide and placebo. However, semaglutide significantly reduced liver steatosis compared with placebo which, together with improvements in liver enzymes and metabolic parameters, suggests a positive impact on disease activity and metabolic profile. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03357380.
© 2021 The Authors. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Comment in
-
Editorial: evolution of GLP-1 receptor agonists as pharmacotherapy for NASH beyond diabetes mellitus and obesity.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Dec;54(11-12):1496-1497. doi: 10.1111/apt.16641. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34741326 No abstract available.
-
Editorial: evolution of GLP-1 receptor agonists as pharmacotherapy for NASH beyond diabetes mellitus and obesity - authors' reply.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Dec;54(11-12):1498. doi: 10.1111/apt.16669. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34741327 No abstract available.
References
-
- Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel Y, Henry L, Wymer M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease – meta‐analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology. 2016;64:73‐84. - PubMed
-
- EASL, EASD, EASO . EASL–EASD–EASO clinical practice guidelines for the management of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64:1388‐1402. - PubMed
-
- Loomba R, Wong R, Fraysse J, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression rates to cirrhosis and progression of cirrhosis to decompensation and mortality: a real world analysis of Medicare data. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2020;51:1149‐1159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
