Intersex Plays a Role in Microbial Homeostasis in the Brown Planthopper
- PMID: 34571752
- PMCID: PMC8465078
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10090875
Intersex Plays a Role in Microbial Homeostasis in the Brown Planthopper
Abstract
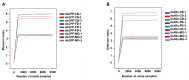
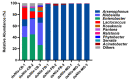
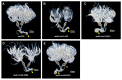
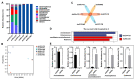
Insects harbor a wide variety of symbiotic microorganisms that are capable of regulating host health and promoting host adaptation to their environment and food sources. However, there is little knowledge concerning the mechanisms that maintain the microbial community homeostasis within insects. In this study, we found that the intersex (ix) gene played an essential role in maintaining microbial homeostasis in the brown planthopper (BPH), Nilaparvata lugens. Injection of the double-strand RNA targeting N. lugens ix (Nlix) into the newly emerged females resulted in abnormal expansion of the copulatory bursa of BPH after mating. Further observation by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) revealed that the abnormally enlarged copulatory bursa resulting from dsNlix treatment was full of microorganisms, while in contrast, the copulatory bursa of dsGFP-treated individuals stored a large number of sperm accompanied by a few bacteria. Moreover, RNA-seq analysis showed that the gene responses to bacteria were remarkably enriched in differentially expressed genes (DEGs). In addition, 16s rRNA sequencing indicated that, compared with control samples, changes in the composition of microbes presented in dsNlix-treated copulatory bursa. Together, our results revealed the immune functions of the Nlix gene in maintaining microbial homeostasis and combating infection in BPH.
Keywords: Nilaparvata lugens; RNA interference; copulation; immune deference; microbiome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Pleiotropic Roles of the Orthologue of the Drosophila melanogaster Intersex Gene in the Brown Planthopper.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 7;12(3):379. doi: 10.3390/genes12030379. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33800002 Free PMC article.
-
Newly introduced Cardinium endosymbiont reduces microbial diversity in the rice brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2020 Nov 26;96(12):fiaa194. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiaa194. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2020. PMID: 32970802
-
NlATG1 Gene Participates in Regulating Autophagy and Fission of Mitochondria in the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens.Front Physiol. 2020 Jan 31;10:1622. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01622. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32082181 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of long noncoding RNA genes and their potential association with fecundity and virulence in rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens.BMC Genomics. 2015 Oct 5;16:749. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1953-y. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26437919 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of diet-associated responses in two rice planthopper species.BMC Genomics. 2020 Aug 17;21(1):565. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06976-2. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32807078 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

