Impact of Oxysterols on Cell Death, Proliferation, and Differentiation Induction: Current Status
- PMID: 34571949
- PMCID: PMC8468221
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10092301
Impact of Oxysterols on Cell Death, Proliferation, and Differentiation Induction: Current Status
Abstract
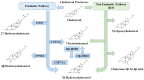
Oxysterols are oxidized derivatives of cholesterol produced by enzymatic activity or non-enzymatic pathways (auto-oxidation). The oxidation processes lead to the synthesis of about 60 different oxysterols. Several oxysterols have physiological, pathophysiological, and pharmacological activities. The effects of oxysterols on cell death processes, especially apoptosis, autophagy, necrosis, and oxiapoptophagy, as well as their action on cell proliferation, are reviewed here. These effects, also observed in several cancer cell lines, could potentially be useful in cancer treatment. The effects of oxysterols on cell differentiation are also described. Among them, the properties of stimulating the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells while inhibiting adipogenic differentiation may be useful in regenerative medicine.
Keywords: apoptosis; autophagy; cell death; differentiation; mesenchymal stem cells; oxiapoptophagy; oxysterols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Faletrov Y.V., Efimova V.S., Horetski M., Tugaeva K.V., Frolova N.S., Lin Q., Isaeva L.V., Rubtsov M.A., Sluchanko N.N., Novikova L.A., et al. New 20-hydroxycholesterol-like compounds with fluorescent NBD or alkyne labels: Synthesis, in silico interactions with proteins and uptake by yeast cells. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2019;227:104850. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2019.104850. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

