Glucocorticoid and PD-1 Cross-Talk: Does the Immune System Become Confused?
- PMID: 34571982
- PMCID: PMC8468592
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10092333
Glucocorticoid and PD-1 Cross-Talk: Does the Immune System Become Confused?
Abstract
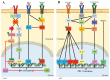
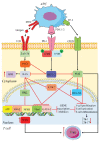
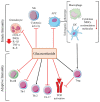
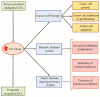
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligands, PD-L1/2, control T cell activation and tolerance. While PD-1 expression is induced upon T cell receptor (TCR) activation or cytokine signaling, PD-L1 is expressed on B cells, antigen presenting cells, and on non-immune tissues, including cancer cells. Importantly, PD-L1 binding inhibits T cell activation. Therefore, the modulation of PD-1/PD-L1 expression on immune cells, both circulating or in a tumor microenvironment and/or on the tumor cell surface, is one mechanism of cancer immune evasion. Therapies that target PD-1/PD-L1, blocking the T cell-cancer cell interaction, have been successful in patients with various types of cancer. Glucocorticoids (GCs) are often administered to manage the side effects of chemo- or immuno-therapy, exerting a wide range of immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects. However, GCs may also have tumor-promoting effects, interfering with therapy. In this review, we examine GC signaling and how it intersects with PD-1/PD-L1 pathways, including a discussion on the potential for GC- and PD-1/PD-L1-targeted therapies to "confuse" the immune system, leading to a cancer cell advantage that counteracts anti-cancer immunotherapy. Therefore, combination therapies should be utilized with an awareness of the potential for opposing effects on the immune system.
Keywords: PD-1/PD-L1; cancer; glucocorticoids; immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined Blockade of IL6 and PD-1/PD-L1 Signaling Abrogates Mutual Regulation of Their Immunosuppressive Effects in the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancer Res. 2018 Sep 1;78(17):5011-5022. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0118. Epub 2018 Jul 2. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29967259
-
Roles of PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway: Signaling, Cancer, and Beyond.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1248:33-59. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-3266-5_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32185706 Review.
-
PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint: Potential target for cancer therapy.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Feb;234(2):1313-1325. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27172. Epub 2018 Sep 7. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30191996 Review.
-
PD-1 and PD-L1 in cancer immunotherapy: clinical implications and future considerations.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(5):1111-1122. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1571892. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30888929 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the tumor microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape.Mol Cancer. 2019 Jan 15;18(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0928-4. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30646912 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mononuclear cell composition and activation in blood and mucosal tissue of eosinophilic esophagitis.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1347259. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1347259. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38318168 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of SGK1 potentiates the anticancer activity of PI3K inhibitor in NSCLC cells through modulation of mTORC1, p‑ERK and β‑catenin signaling.Biomed Rep. 2023 Oct 13;19(6):94. doi: 10.3892/br.2023.1676. eCollection 2023 Dec. Biomed Rep. 2023. PMID: 37901878 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of High Efficacy Multiple Sclerosis Disease Modifying Drugs on the Immune Synapse: A Systematic Review.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(7):536-551. doi: 10.2174/0113816128288102240131053205. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38343058
-
Survival Mechanisms of Metastatic Melanoma Cells: The Link between Glucocorticoids and the Nrf2-Dependent Antioxidant Defense System.Cells. 2023 Jan 26;12(3):418. doi: 10.3390/cells12030418. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blockade of the PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Pathway Improves Infection Outcomes and Enhances Fungicidal Host Defense in a Murine Model of Invasive Pulmonary Mucormycosis.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 18;13:838344. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.838344. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35251033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wojtukiewicz M.Z., Rek M.M., Karpowicz K., Gorska M., Politynska B., Wojtukiewicz A.M., Moniuszko M., Radziwon P., Tucker S.C., Honn K.V. Inhibitors of immune checkpoints-PD-1, PD-L1, CTLA-4-new opportunities for cancer patients and a new challenge for internists and general practitioners. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s10555-021-09976-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

