Lipid Polymorphism of the Subchloroplast-Granum and Stroma Thylakoid Membrane-Particles. I. 31P-NMR Spectroscopy
- PMID: 34572003
- PMCID: PMC8470346
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10092354
Lipid Polymorphism of the Subchloroplast-Granum and Stroma Thylakoid Membrane-Particles. I. 31P-NMR Spectroscopy
Abstract
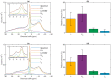
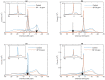
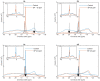
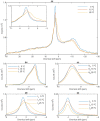
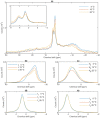
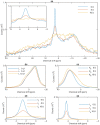
Build-up of the energized state of thylakoid membranes and the synthesis of ATP are warranted by organizing their bulk lipids into a bilayer. However, the major lipid species of these membranes, monogalactosyldiacylglycerol, is a non-bilayer lipid. It has also been documented that fully functional thylakoid membranes, in addition to the bilayer, contain an inverted hexagonal (HII) phase and two isotropic phases. To shed light on the origin of these non-lamellar phases, we performed 31P-NMR spectroscopy experiments on sub-chloroplast particles of spinach: stacked, granum and unstacked, stroma thylakoid membranes. These membranes exhibited similar lipid polymorphism as the whole thylakoids. Saturation transfer experiments, applying saturating pulses at characteristic frequencies at 5 °C, provided evidence for distinct lipid phases-with component spectra very similar to those derived from mathematical deconvolution of the 31P-NMR spectra. Wheat-germ lipase treatment of samples selectively eliminated the phases exhibiting sharp isotropic peaks, suggesting easier accessibility of these lipids compared to the bilayer and the HII phases. Gradually increasing lipid exchanges were observed between the bilayer and the two isotropic phases upon gradually elevating the temperature from 5 to 35 °C, suggesting close connections between these lipid phases. Data concerning the identity and structural and functional roles of different lipid phases will be presented in the accompanying paper.
Keywords: 31P-NMR; DEM—dynamic exchange model; HII phase; bilayer membrane; grana; isotropic phase; non-bilayer lipids; non-lamellar lipid phases; structural flexibility; thylakoid membranes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural Entities Associated with Different Lipid Phases of Plant Thylakoid Membranes-Selective Susceptibilities to Different Lipases and Proteases.Cells. 2022 Aug 28;11(17):2681. doi: 10.3390/cells11172681. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078087 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid polymorphism of plant thylakoid membranes. The dynamic exchange model - facts and hypotheses.Physiol Plant. 2025 Mar-Apr;177(2):e70230. doi: 10.1111/ppl.70230. Physiol Plant. 2025. PMID: 40251902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Polymorphism of the Subchloroplast-Granum and Stroma Thylakoid Membrane-Particles. II. Structure and Functions.Cells. 2021 Sep 9;10(9):2363. doi: 10.3390/cells10092363. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572012 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid polymorphism in chloroplast thylakoid membranes - as revealed by 31P-NMR and time-resolved merocyanine fluorescence spectroscopy.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 17;7(1):13343. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13574-y. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29042649 Free PMC article.
-
Role of MGDG and Non-bilayer Lipid Phases in the Structure and Dynamics of Chloroplast Thylakoid Membranes.Subcell Biochem. 2016;86:127-57. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-25979-6_6. Subcell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27023234 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural Entities Associated with Different Lipid Phases of Plant Thylakoid Membranes-Selective Susceptibilities to Different Lipases and Proteases.Cells. 2022 Aug 28;11(17):2681. doi: 10.3390/cells11172681. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078087 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Phase Behaviour of the Curvature Region of Thylakoid Membranes of Spinacia oleracea.Physiol Plant. 2025 May-Jun;177(3):e70289. doi: 10.1111/ppl.70289. Physiol Plant. 2025. PMID: 40525547 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid polymorphism of plant thylakoid membranes. The dynamic exchange model - facts and hypotheses.Physiol Plant. 2025 Mar-Apr;177(2):e70230. doi: 10.1111/ppl.70230. Physiol Plant. 2025. PMID: 40251902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Polymorphism of the Subchloroplast-Granum and Stroma Thylakoid Membrane-Particles. II. Structure and Functions.Cells. 2021 Sep 9;10(9):2363. doi: 10.3390/cells10092363. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34572012 Free PMC article.
-
Role of isotropic lipid phase in the fusion of photosystem II membranes.Photosynth Res. 2024 Aug;161(1-2):127-140. doi: 10.1007/s11120-024-01097-3. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Photosynth Res. 2024. PMID: 38662326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seddon J.M., Templer R.H. Chapter 3—Polymorphism of Lipid-Water Systems. In: Lipowsky R., Sackmann E., editors. Handbook of Biological Physics. Volume 1. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 1995. pp. 97–160.
-
- Williams W.P. The Physical Properties of Thylakoid Membrane Lipids and Their Relation to Photosynthesis. In: Paul-André S., Norio M., editors. Lipids in Photosynthesis: Structure, Function and Genetics. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 1998. pp. 103–118.
-
- Douce R., Joyard J. Biosynthesis of Thylakoid Membrane Lipids. In: Ort D.R., Yocum C.F., Heichel I.F., editors. Oxygenic Photosynthesis: The Light Reactions. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 1996. pp. 69–101.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 19-13637S/Grantová Agentura České Republiky
- K 128679/Hungarian Scientific Research Fund
- CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000797/SustES - Adaptation strategies for sustainable ecosystem services and food security under adverse environmental conditions
- SGS02/PřF/2021/Ostravská Univerzita v Ostravě
- 07359/2019/RRC/Silesian Region
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

