Identifying GPSM Family Members as Potential Biomarkers in Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis
- PMID: 34572330
- PMCID: PMC8471503
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9091144
Identifying GPSM Family Members as Potential Biomarkers in Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis
Abstract
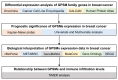
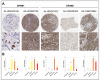
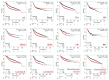
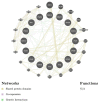
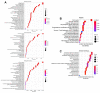
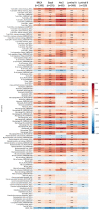
G-protein signaling modulators (GPSMs) are a class of proteins involved in the regulation of G protein-coupled receptors, the most abundant family of cell-surface receptors that are crucial in the development of various tumors, including breast cancer. This study aims to identify the potential therapeutic and prognostic roles of GPSMs in breast cancer. Oncomine and UALCAN databases were queried to determine GPSM expression levels in breast cancer tissues compared to normal samples. Survival analysis was conducted to reveal the prognostic significance of GPSMs in individuals with breast cancer. Functional enrichment analysis was performed using cBioPortal and MetaCore platforms. Finally, the association between GPSMs and immune infiltration cells in breast cancer was identified using the TIMER server. The experimental results then showed that all GPSM family members were significantly differentially expressed in breast cancer according to Oncomine and UALCAN data. Their expression levels were also associated with advanced tumor stages, and GPSM2 was found to be related to worse distant metastasis-free survival in patients with breast cancer. Functional enrichment analysis indicated that GPSMs were largely involved in cell division and cell cycle pathways. Finally, GPSM3 expression was correlated with the infiltration of several immune cells. Members of the GPSM class were differentially expressed in breast cancer. In conclusion, expression of GPSM2 was linked with worse distant metastasis-free outcomes, and hence could potentially serve as a prognostic biomarker. Furthermore, GPSM3 has potential to be a possible target for immunotherapy for breast cancer.
Keywords: G-protein signaling modulator; biomarker; breast cancer; functional enrichment analysis; gene expression; immunotherapy; survival analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
G-Protein Signaling Modulator 2 as a Potential Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer: Integrative Analysis Using Genetic Profiling and Pan-Cancer Studies.Genes (Basel). 2024 Apr 9;15(4):474. doi: 10.3390/genes15040474. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674408 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of RUNX and TGF-β Mediated Regulation of Immune Cell Infiltration in Breast Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 18;9:730380. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.730380. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34485309 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the expression, prognostic significance, and function of FAM83 family members in breast cancer.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Jun 1;20(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02636-9. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35650627 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Prognostic Biomarkers of NIMA (Never in Mitosis, Gene A)-Related Kinase (NEK) Family Members in Breast Cancer.J Pers Med. 2021 Oct 26;11(11):1089. doi: 10.3390/jpm11111089. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34834441 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic summarization of the expression profiles and prognostic roles of the dishevelled gene family in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Sep;8(9):e1384. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1384. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32588988 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
G-Protein Signaling Modulator 2 as a Potential Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer: Integrative Analysis Using Genetic Profiling and Pan-Cancer Studies.Genes (Basel). 2024 Apr 9;15(4):474. doi: 10.3390/genes15040474. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674408 Free PMC article.
-
In-silico discovery of type-2 diabetes-causing host key genes that are associated with the complexity of monkeypox and repurposing common drugs.Brief Bioinform. 2025 May 1;26(3):bbaf215. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaf215. Brief Bioinform. 2025. PMID: 40370100 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-646 inhibited cell proliferation and migration by targeting P62 in glioma.Cell Adh Migr. 2025 Dec;19(1):2515763. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2025.2515763. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Cell Adh Migr. 2025. PMID: 40590381 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of MAD2L1 as a Potential Biomarker in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Jan 28;2022:9868022. doi: 10.1155/2022/9868022. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35132379 Free PMC article.
-
Key Cell-in-Cell Related Genes are Identified by Bioinformatics and Experiments in Glioblastoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2024 Sep 5;16:1109-1130. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S475513. eCollection 2024. Cancer Manag Res. 2024. PMID: 39253064 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

