Correlation of Pulse Wave Transit Time with Pulmonary Artery Pressure in a Porcine Model of Pulmonary Hypertension
- PMID: 34572397
- PMCID: PMC8467418
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9091212
Correlation of Pulse Wave Transit Time with Pulmonary Artery Pressure in a Porcine Model of Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
For the non-invasive assessment of pulmonary artery pressure (PAP), surrogates like pulse wave transit time (PWTT) have been proposed. The aim of this study was to invasively validate for which kind of PAP (systolic, mean, or diastolic) PWTT is the best surrogate parameter. To assess both PWTT and PAP in six healthy pigs, two pulmonary artery Mikro-Tip™ catheters were inserted into the pulmonary vasculature at a fixed distance: one in the pulmonary artery trunk, and a second one in a distal segment of the pulmonary artery. PAP was raised using the thromboxane A2 analogue U46619 (TXA) and by hypoxic vasoconstriction. There was a negative linear correlation between PWTT and systolic PAP (r = 0.742), mean PAP (r = 0.712) and diastolic PAP (r = 0.609) under TXA. During hypoxic vasoconstriction, the correlation coefficients for systolic, mean, and diastolic PAP were consistently higher than for TXA-induced pulmonary hypertension (r = 0.809, 0.778 and 0.734, respectively). Estimation of sPAP, mPAP, and dPAP using PWTT is feasible, nevertheless slightly better correlation coefficients were detected for sPAP compared to dPAP. In this study we establish the physiological basis for future methods to obtain PAP by non-invasively measured PWTT.
Keywords: pulmonary artery pressure (PAP); pulmonary hypertension (PH); pulse arrival time (PAT); pulse wave transit time (PWTT); pulse wave velocity (PWV).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
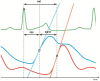




References
-
- Galiè N., Humbert M., Vachiery J.-L., Gibbs S., Lang I., Torbicki A., Simonneau G., Peacock A., Vonk Noordegraaf A., Beghetti M., et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) Eur. Heart J. 2016;37:67–119. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv317. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schäfer M., Wilson N., Ivy D.D., Ing R., Abman S., Browne L.P., Morgan G., Ross M., McLennan D., Barker A.J., et al. Noninvasive wave intensity analysis predicts functional worsening in children with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018;315:H968–H977. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00227.2018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jernstedt G.C., Newcomer J.P. Blood pressure and pulse wave velocity measurement for operant conditioning of autonomic responding. Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. 1974;6:393–397. doi: 10.3758/BF03200386. - DOI
-
- Peter L., Noury N., Cerny M. A review of methods for non-invasive and continuous blood pressure monitoring: Pulse transit time method is promising? IRBM. 2014;35:271–282. doi: 10.1016/j.irbm.2014.07.002. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

