Inhibition of Aminoglycoside 6'- N-acetyltransferase Type Ib (AAC(6')-Ib): Structure-Activity Relationship of Substituted Pyrrolidine Pentamine Derivatives as Inhibitors
- PMID: 34572404
- PMCID: PMC8471502
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9091218
Inhibition of Aminoglycoside 6'- N-acetyltransferase Type Ib (AAC(6')-Ib): Structure-Activity Relationship of Substituted Pyrrolidine Pentamine Derivatives as Inhibitors
Abstract
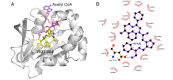
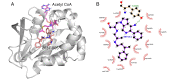
The aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase type Ib (AAC(6')-Ib) is a common cause of resistance to amikacin and other aminoglycosides in Gram-negatives. Utilization of mixture-based combinatorial libraries and application of the positional scanning strategy identified an inhibitor of AAC(6')-Ib. This inhibitor's chemical structure consists of a pyrrolidine pentamine scaffold substituted at four locations (R1, R3, R4, and R5). The substituents are two S-phenyl groups (R1 and R4), an S-hydroxymethyl group (R3), and a 3-phenylbutyl group (R5). Another location, R2, does not have a substitution, but it is named because its stereochemistry was modified in some compounds utilized in this study. Structure-activity relationship (SAR) analysis using derivatives with different functionalities, modified stereochemistry, and truncations was carried out by assessing the effect of the addition of each compound at 8 µM to 16 µg/mL amikacin-containing media and performing checkerboard assays varying the concentrations of the inhibitor analogs and the antibiotic. The results show that: (1) the aromatic functionalities at R1 and R4 are essential, but the stereochemistry is essential only at R4; (2) the stereochemical conformation at R2 is critical; (3) the hydroxyl moiety at R3 as well as stereoconformation are required for full inhibitory activity; (4) the phenyl functionality at R5 is not essential and can be replaced by aliphatic groups; (5) the location of the phenyl group on the butyl carbon chain at R5 is not essential; (6) the length of the aliphatic chain at R5 is not critical; and (7) all truncations of the scaffold resulted in inactive compounds. Molecular docking revealed that all compounds preferentially bind to the kanamycin C binding cavity, and binding affinity correlates with the experimental data for most of the compounds evaluated. The SAR results in this study will serve as the basis for the design of new analogs in an effort to improve their ability to induce phenotypic conversion to susceptibility in amikacin-resistant pathogens.
Keywords: Acinetobacter; acetyltransferase; aminoglycoside resistance; aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes; structure–activity relationship.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure-Activity Relationship of Pyrrolidine Pentamine Derivatives as Inhibitors of the Aminoglycoside 6'-N-Acetyltransferase Type Ib.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 19;13(7):672. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070672. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061354 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-activity relationship of pyrrolidine pentamine derivatives as inhibitors of the aminoglycoside 6'- N -acetyltransferase type Ib.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 14:2024.05.14.594018. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.14.594018. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 19;13(7):672. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070672. PMID: 38798525 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Identification of a small molecule inhibitor of the aminoglycoside 6'-N-acetyltransferase type Ib [AAC(6')-Ib] using mixture-based combinatorial libraries.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018 May;51(5):752-761. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.01.019. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018. PMID: 29410367 Free PMC article.
-
Amikacin: Uses, Resistance, and Prospects for Inhibition.Molecules. 2017 Dec 19;22(12):2267. doi: 10.3390/molecules22122267. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29257114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studies on aminoglycoside antibiotics: enzymic mechanism of resistance and genetics.Jpn J Antibiot. 1979 Dec;32 Suppl:S1-14. Jpn J Antibiot. 1979. PMID: 233022 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure-Activity Relationship of Pyrrolidine Pentamine Derivatives as Inhibitors of the Aminoglycoside 6'-N-Acetyltransferase Type Ib.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 19;13(7):672. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070672. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061354 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting Amikacin Resistance in Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria with Cadmium and Pyrithione.Curr Microbiol. 2025 Jul 16;82(9):389. doi: 10.1007/s00284-025-04372-1. Curr Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40668405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Restoring susceptibility to aminoglycosides: identifying small molecule inhibitors of enzymatic inactivation.RSC Med Chem. 2023 Jul 21;14(9):1591-1602. doi: 10.1039/d3md00226h. eCollection 2023 Sep 19. RSC Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37731693 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- De Man T.J.B., Lutgring J.D., Lonsway D.R., Anderson K.F., Kiehlbauch J.A., Chen L., Walters M.S., Sjolund-Karlsson M., Rasheed J.K., Kallen A., et al. Genomic analysis of a pan-resistant isolate of Klebsiella pneumoniae, United States 2016. mBio. 2018;9:e00440-18. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00440-18. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2017. [(accessed on 1 September 2021)]. Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2017/bacteria-antibiotics-n...
-
- Tolmasky M.E. Strategies to prolong the useful life of existing antibiotics and help overcoming the antibiotic resistance crisis. In: Rhaman A., editor. Frontiers in Clinical Drug Research-Anti Infectives. Volume 1. Bentham Books; Sharjah, United Arab Emirates: 2017. pp. 1–27.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

