Emergence of Cardiac Glycosides as Potential Drugs: Current and Future Scope for Cancer Therapeutics
- PMID: 34572488
- PMCID: PMC8465509
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11091275
Emergence of Cardiac Glycosides as Potential Drugs: Current and Future Scope for Cancer Therapeutics
Abstract
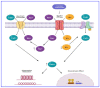
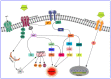
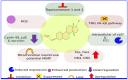
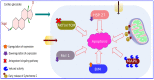
Cardiac glycosides are natural sterols and constitute a group of secondary metabolites isolated from plants and animals. These cardiotonic agents are well recognized and accepted in the treatment of various cardiac diseases as they can increase the rate of cardiac contractions by acting on the cellular sodium potassium ATPase pump. However, a growing number of recent efforts were focused on exploring the antitumor and antiviral potential of these compounds. Several reports suggest their antitumor properties and hence, today cardiac glycosides (CG) represent the most diversified naturally derived compounds strongly recommended for the treatment of various cancers. Mutated or dysregulated transcription factors have also gained prominence as potential therapeutic targets that can be selectively targeted. Thus, we have explored the recent advances in CGs mediated cancer scope and have considered various signaling pathways, molecular aberration, transcription factors (TFs), and oncogenic genes to highlight potential therapeutic targets in cancer management.
Keywords: cancer therapy; cardiac glycosides; in vitro and in vivo anticancer activities; therapeutic target; transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel therapeutic applications of cardiac glycosides.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008 Nov;7(11):926-35. doi: 10.1038/nrd2682. Epub 2008 Oct 24. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008. PMID: 18948999 Review.
-
Anticancer and Immunogenic Properties of Cardiac Glycosides.Molecules. 2017 Nov 8;22(11):1932. doi: 10.3390/molecules22111932. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 29117117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiac glycosides inhibit cancer through Na/K-ATPase-dependent cell death induction.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;182:114226. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114226. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32976831 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects and Therapeutic Applications of Cardiac Glycosides in Cancer Remediation.ACS Comb Sci. 2020 Nov 9;22(11):543-553. doi: 10.1021/acscombsci.0c00082. Epub 2020 Aug 24. ACS Comb Sci. 2020. PMID: 32786321 Review.
-
Cardiac Glycosides as Immune System Modulators.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 29;11(5):659. doi: 10.3390/biom11050659. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33947098 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular Modes of Action of an Aqueous Nerium oleander Extract in Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo.Molecules. 2023 Feb 16;28(4):1871. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041871. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838857 Free PMC article.
-
Convallatoxin suppresses osteosarcoma cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and enhances osteogenic differentiation by downregulating parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTHR1) expression and inactivating Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Bioengineered. 2022 May;13(5):13280-13292. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2080363. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35635031 Free PMC article.
-
Lanatoside C Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Human Prostate Cancer Cells Through the TNF/IL-17 Signaling Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 12;26(6):2558. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062558. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141200 Free PMC article.
-
PBI-05204, a supercritical CO2 extract of Nerium oleander, suppresses glioblastoma stem cells by inhibiting GRP78 and inducing programmed necroptotic cell death.Neoplasia. 2024 Aug;54:101008. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2024.101008. Epub 2024 May 31. Neoplasia. 2024. PMID: 38823209 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanistic role of cardiac glycosides in DNA damage response and repair signaling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Aug 16;80(9):250. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04910-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37584722 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

