Enhanced Antibacterial Potential of Amoxicillin against Helicobacter pylori Mediated by Lactobionic Acid Coated Zn-MOFs
- PMID: 34572653
- PMCID: PMC8470299
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10091071
Enhanced Antibacterial Potential of Amoxicillin against Helicobacter pylori Mediated by Lactobionic Acid Coated Zn-MOFs
Abstract
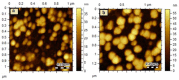
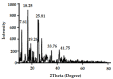
H. pylori (Helicobacter pylori) causes a common chronic infectious disease and infects around 4.4 billion people worldwide. H. pylori was classified as a member of the primary class of stomach cancer (stomach adenocarcinoma). Hence, this study was conducted to design a novel lactobionic acid (LBA)-coated Zn-MOFs to enhance bactericidal activity of Amoxicillin (AMX) against H. pylori. The synthesized Zn-MOFs were characterized by various techniques which included Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS), Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy, Powder X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, and atomic force microscope. They were capable of encapsulating an increased amount of AMX and investigated for their efficacy to enhance the antibacterial potential of their loaded drug candidate. Interestingly, it was found that LBA-coated Zn-MOFs significantly reduced the IC50, MIC, and MBIC values of AMX against H. pylori. Morphological investigation of treated bacterial cells further authenticated the above results as LBA-coated Zn-MOFs-treated cells underwent complete distortion compared with non-coated AMX loaded Zn-MOFs. Based on the results of the study, it can be suggested that LBA-coated Zn-MOFs may be an effective alternate candidate to provide new perspective for the treatment of H. pylori infections.
Keywords: Amoxicillin; H. pylori; lactobionic acid; metal organic frameworks (MOFs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Improving curcumin bactericidal potential against multi-drug resistant bacteria via its loading in polydopamine coated zinc-based metal-organic frameworks.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):2159587. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2159587. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 36718806 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Ribose-Coated Copper-Based Metal-Organic Framework for Enhanced Antibacterial Potential of Chloramphenicol against Multi-Drug Resistant Bacteria.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Nov 29;10(12):1469. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10121469. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943681 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of chitosan coated metal organic frameworks (MOFs) for increasing vancomycin bactericidal potentials against resistant S. aureus strain.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019 Dec;105:110111. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110111. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019. PMID: 31546392
-
Amoxicillin-docosahexaenoic acid encapsulated chitosan-alginate nanoparticles as a delivery system with enhanced biocidal activities against Helicobacter pylori and improved ulcer healing.Front Microbiol. 2023 Feb 9;14:1083330. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1083330. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36846798 Free PMC article.
-
Floating-bioadhesive gastroretentive Caesalpinia pulcherrima-based beads of amoxicillin trihydrate for Helicobacter pylori eradication.Drug Deliv. 2016;23(2):405-19. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.916766. Epub 2014 May 28. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 24870198
Cited by
-
Improving curcumin bactericidal potential against multi-drug resistant bacteria via its loading in polydopamine coated zinc-based metal-organic frameworks.Drug Deliv. 2023 Dec;30(1):2159587. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2159587. Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 36718806 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Metal-Organic Framework in Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetes.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 5;12(9):1240. doi: 10.3390/biom12091240. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hesperidin-, Curcumin-, and Amphotericin B- Based Nano-Formulations as Potential Antibacterials.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 May 20;11(5):696. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11050696. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625340 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in metal-organic frameworks for antibacterial applications: mechanisms and emerging strategies.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 28;15(33):26710-26727. doi: 10.1039/d5ra02955d. eCollection 2025 Jul 25. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40727299 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle formulations for therapeutic delivery, pathogen imaging and theranostic applications in bacterial infections.Theranostics. 2023 Mar 5;13(5):1545-1570. doi: 10.7150/thno.82790. eCollection 2023. Theranostics. 2023. PMID: 37056563 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wilson W. Prevention of infective endocarditis: Guidelines from the American heart association: A guideline from the American heart association rheumatic fever, endocarditis, and Kawasaki disease committee, council on cardiovascular disease in the young, and the council on clinical cardiology, council on cardiovascular surgery and anesthesia, and the quality of care and outcomes research interdisciplinary working group. Circulation. 2007;116:1736–1754. - PubMed
-
- Akhavan B.J., Khanna N.R., Vijhani P. Amoxicillin. StatPearls Publishing; San Francisco, CA, USA: 2020. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

