Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Applications in Biomedical Sector
- PMID: 34572676
- PMCID: PMC8465024
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10091094
Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Applications in Biomedical Sector
Abstract
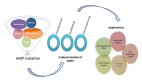
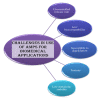
In a report by WHO (2014), it was stated that antimicrobial resistance is an arising challenge that needs to be resolved. This resistance is a critical issue in terms of disease or infection treatment and is usually caused due to mutation, gene transfer, long-term usage or inadequate use of antimicrobials, survival of microbes after consumption of antimicrobials, and the presence of antimicrobials in agricultural feeds. One of the solutions to this problem is antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), which are ubiquitously present in the environment. These peptides are of concern due to their special mode of action against a wide spectrum of infections and health-related problems. The biomedical field has the highest need of AMPs as it possesses prominent desirable activity against HIV-1, skin cancer, breast cancer, in Behcet's disease treatment, as well as in reducing the release of inflammatory cells such as TNFα, IL-8, and IL-1β, enhancing the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and GM-CSF, and in wound healing properties. This review has highlighted all the major functions and applications of AMPs in the biomedical field and concludes the future potential of AMPs.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; anticancer; antimicrobial activity; antimicrobial peptides; biomedical application; functions of AMP; immunomodulatory effect; implementation techniques; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Systematic Review of the Design and Applications of Antimicrobial Peptides in Wound Healing.Cureus. 2024 Apr 13;16(4):e58178. doi: 10.7759/cureus.58178. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38741875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides: Challenging Journey to the Pharmaceutical, Biomedical, and Cosmeceutical Use.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 20;24(10):9031. doi: 10.3390/ijms24109031. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collagen tethering of synthetic human antimicrobial peptides cathelicidin LL37 and its effects on antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity.Acta Biomater. 2017 Apr 1;52:9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.12.047. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28017866
-
Antimicrobial peptides - Unleashing their therapeutic potential using nanotechnology.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Apr;232:107990. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107990. Epub 2021 Sep 28. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 34592202 Review.
-
Antimicrobial synergy of monolaurin lipid nanocapsules with adsorbed antimicrobial peptides against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms in vitro is absent in vivo.J Control Release. 2019 Jan 10;293:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.11.018. Epub 2018 Nov 19. J Control Release. 2019. PMID: 30465823
Cited by
-
Effect of Bioactive Peptides on Gut Microbiota and Their Relations to Human Health.Foods. 2024 Jun 13;13(12):1853. doi: 10.3390/foods13121853. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38928795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Effects of Synthetic Triblock Amphiphilic Short Antimicrobial Peptides on Human Lung Adenocarcinoma.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Apr 24;14(5):929. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14050929. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35631515 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug-Resistant Microbial Therapy Using Antimicrobial Peptides and the CRISPR/Cas9 System.Vet Med (Auckl). 2022 Aug 11;13:173-190. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S366533. eCollection 2022. Vet Med (Auckl). 2022. PMID: 35983086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Hepcidin Isoform Jd-Hep from the Sin Croaker Johnius dussumieri (Cuvier, 1830): Recombinant Expression and Insights into the Antibacterial Property and Modes of Action.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2025 Feb 19;27(2):52. doi: 10.1007/s10126-025-10426-z. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2025. PMID: 39969620
-
Investigation of the Antibacterial Effectiveness of Hybrid Recombinant Bacteriocins Circular Enterocin and Pyocin L1 Derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterococcus faecalis.Biochem Genet. 2025 Jun 13. doi: 10.1007/s10528-025-11149-5. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 40512297
References
-
- Gupta A., Gupta R., Singh R.L. Principles and Applications of Environmental Biotechnology for a Sustainable Future. Springer; Singapore: 2017. Microbes and environment; pp. 43–84.
-
- Grace J.L., Huang J.X., Cheah S.E., Truong N.P., Cooper M.A., Li J., Davis T.P., Quinn J.F., Velkov T., Whittaker M.R. Antibacterial low molecular weight cationic polymers: Dissecting the contribution of hydrophobicity, chain length and charge to activity. RSC Adv. 2016;6:15469–15477. doi: 10.1039/C5RA24361K. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed M.S. Ph.D. Thesis. Florida International University; Miami, FL, USA: Jun 12, 2017. Synthesis of Antimicrobial Polymers to Overcome Antimicrobial Resistance.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

