Genomic Investigation of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST113 Strains Isolated from Tertiary Care Hospitals in Pakistan
- PMID: 34572703
- PMCID: PMC8465543
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10091121
Genomic Investigation of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ST113 Strains Isolated from Tertiary Care Hospitals in Pakistan
Abstract
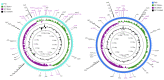
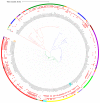
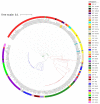
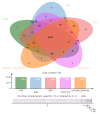
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a multi-drug resistant and opportunistic pathogen. The emergence of new clones of MRSA in both healthcare settings and the community warrants serious attention and epidemiological surveillance. However, epidemiological data of MRSA isolates from Pakistan are limited. We performed a whole-genome-based comparative analysis of two (P10 and R46) MRSA strains isolated from two provinces of Pakistan to understand the genetic diversity, sequence type (ST), and distribution of virulence and antibiotic-resistance genes. The strains belong to ST113 and harbor the SCCmec type IV encoding mecA gene. Both the strains contain two plasmids, and three and two complete prophage sequences are present in P10 and R46, respectively. The specific antibiotic resistance determinants in P10 include two aminoglycoside-resistance genes, aph(3')-IIIa and aad(6), a streptothrin-resistance gene sat-4, a tetracycline-resistance gene tet(K), a mupirocin-resistance gene mupA, a point mutation in fusA conferring resistance to fusidic acid, and in strain R46 a specific plasmid associated gene ant(4')-Ib. The strains harbor many virulence factors common to MRSA. However, no Panton-Valentine leucocidin (lukF-PV/lukS-PV) or toxic shock syndrome toxin (tsst) genes were detected in any of the genomes. The phylogenetic relationship of P10 and R46 with other prevailing MRSA strains suggests that ST113 strains are closely related to ST8 strains and ST113 strains are a single-locus variant of ST8. These findings provide important information concerning the emerging MRSA clone ST113 in Pakistan and the sequenced strains can be used as reference strains for the comparative genomic analysis of other MRSA strains in Pakistan and ST113 strains globally.
Keywords: ST113; antibiotic-resistance; comparative genome analysis; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; multi-locus sequence type; whole-genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Liang Y., Tu C., Tan C., El-Sayed Ahmed M.A.E.-G., Dai M., Xia Y., Liu Y., Zhong L.-L., Shen C., Chen G., et al. Antimicrobial resistance, virulence genes profiling and molecular relatedness of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from hospitalized patients in Guangdong Province, China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019;12:447–459. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S192611. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ullah N., Raza T., Dar H.A., Shehroz M., Zaheer T., Naz K., Ali A. Whole-genome sequencing of a new sequence type (ST5352) strain of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from a hospital in Pakistan. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019;19:161–163. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2019.09.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brown-Jaque M., Rodriguez Oyarzun L., Cornejo-Sánchez T., Martín-Gomez M.T., Gartner S., De Gracia J., Rovira S., Alvarez A., Jofre J., González-López J.J., et al. Detection of Bacteriophage Particles Containing Antibiotic Resistance Genes in the Sputum of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Front. Microbiol. 2018;9:856. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00856. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

