Use of Dalbavancin in Skin, Bone and Joint Infections: A Real-Life Experience in an Italian Center
- PMID: 34572711
- PMCID: PMC8468778
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10091129
Use of Dalbavancin in Skin, Bone and Joint Infections: A Real-Life Experience in an Italian Center
Abstract
Dalbavancin is a lipoglycopeptide approved for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSI). The aim of the study was to evaluate the efficacy and safety in all patients who received at least one administration of dalbavancin.
Methods: We carried out a retrospective study of the use of dalbavancin in 55 patients at the Azienda Ospedaliera Ospedali Riuniti Umberto I (Ancona, Italy) from February 2017 to May 2020 and compared "on label" and "off label" use of dalbavancin in ABSSSI and non-ABSSSI.
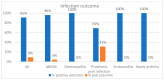
Results: A total of 55 patients were included in the study. The median age was 61 years; 51% had ABSSSI; 24% had prosthetic joint infections, and 14% had osteomyelitis. A total of 53% received a single 1500 mg infusion of dalbavancin, and 18% received a second dose 14 days later; 24% of patients received further doses at 14-day intervals. In 91% of cases, patients achieved clinical objectives with dalbavancin: 96% of patients with ABSSSI and 69% of those with prosthetic joint infections.
Conclusions: Dalbavancin was shown to have an excellent tolerability profile and to be a highly successful therapeutic approach even in those cases treated "off-label".
Keywords: ABSSSI; dalbavancin; osteomyelitis; prosthetic joint infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The funding sponsors did not have any role in the choice of research project; design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish.
Figures
References
-
- David M.Z., Dryden M., Gottlieb T., Tattevin P., Gould I.M. Recently Approved Antibacterials for Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) and Other Gram-Positive Pathogens: The Shock of the New. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents. 2017;50:303–307. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2017.05.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Simonetti O., Lucarini G., Morroni G., Orlando F., Lazzarini R., Zizzi A., Brescini L., Provinciali M., Giacometti A., Offidani A., et al. New Evidence and Insights on Dalbavancin and Wound Healing in a Mouse Model of Skin Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020;64:e02062-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02062-19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources