LyeTx I-b Peptide Attenuates Tumor Burden and Metastasis in a Mouse 4T1 Breast Cancer Model
- PMID: 34572719
- PMCID: PMC8466574
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10091136
LyeTx I-b Peptide Attenuates Tumor Burden and Metastasis in a Mouse 4T1 Breast Cancer Model
Abstract
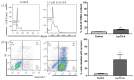
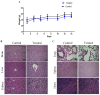
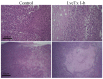
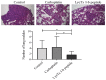
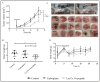
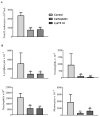
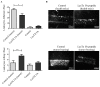
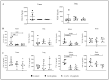
Cationic anticancer peptides have exhibited potent anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory effects in neoplastic illness conditions. LyeTx I-b is a synthetic peptide derived from Lycosa erythrognatha spider venom that previously showed antibiotic activity in vitro and in vivo. This study focused on the effects of LyeTxI-b on a 4T1 mouse mammary carcinoma model. Mice with a palpable tumor in the left flank were subcutaneously or intratumorally injected with LyeTx I-b (5 mg/kg), which significantly decreased the tumor volume and metastatic nodules. Histological analyses showed a large necrotic area in treated primary tumors compared to the control. LyeTxI-b reduced tumor growth and lung metastasis in the 4T1 mouse mammary carcinoma model with no signs of toxicity in healthy or cancerous mice. The mechanism of action of LyeTx I-b on the 4T1 mouse mammary carcinoma model was evaluated in vitro and is associated with induction of apoptosis and cell proliferation inhibition. Furthermore, LyeTx I-b seems to be an efficient regulator of the 4T1 tumor microenvironment by modulating several cytokines, such as TGF-β, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10, in primary tumor and lung, spleen, and brain. LyeTx I-b also plays a role in leukocytes rolling and adhesion into spinal cord microcirculation and in the number of circulating leukocytes. These data suggest a potent antineoplastic efficacy ofLyeTx I-b.
Keywords: Lycosa erythrognatha; LyeTx I-b peptide; anticancer activity of LyeTx I-b; breast cancer; cytokines; immunomodulation; leukocyte recruitment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this article certify that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
LyeTxI-b, a Synthetic Peptide Derived From a Spider Venom, Is Highly Active in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells and Acts Synergistically With Cisplatin.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 May 4;9:876833. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.876833. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35601827 Free PMC article.
-
The synthetic peptide LyeTxI-b derived from Lycosa erythrognatha spider venom is cytotoxic to U-87 MG glioblastoma cells.Amino Acids. 2019 Mar;51(3):433-449. doi: 10.1007/s00726-018-2678-4. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Amino Acids. 2019. PMID: 30449002
-
Comparative Structural and Biophysical Investigation of Lycosa erythrognatha Toxin I (LyeTx I) and Its Analog LyeTx I-b.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Jan 10;14(1):66. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14010066. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39858352 Free PMC article.
-
Pegylated LyeTx I-b peptide is effective against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in an in vivo model of pneumonia and shows reduced toxicity.Int J Pharm. 2021 Nov 20;609:121156. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121156. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34624440
-
A short synthetic peptide, based on LyeTx I from Lycosa erythrognatha venom, shows potential to treat pneumonia caused by carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii without detectable resistance.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2021 Jul;74(7):425-434. doi: 10.1038/s41429-021-00421-6. Epub 2021 May 10. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2021. PMID: 33972716
Cited by
-
LyeTxI-b, a Synthetic Peptide Derived From a Spider Venom, Is Highly Active in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells and Acts Synergistically With Cisplatin.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 May 4;9:876833. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.876833. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35601827 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and validating the optimal panel of housekeeping genes for 4T1 breast carcinoma and metastasis studies in mice.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 2;14(1):26476. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77126-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39488625 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer and Antioxidant Activities of the Root Extract of the Carnivorous Pitcher Plant Sarracenia purpurea.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jun 23;11(13):1668. doi: 10.3390/plants11131668. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35807620 Free PMC article.
-
Venom-derived peptides for breaking through the glass ceiling of drug development.Front Chem. 2024 Sep 26;12:1465459. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1465459. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39398192 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytotoxic, Antibacterial, and Antioxidant Activities of the Leaf Extract of Sinningia bullata.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 14;12(4):859. doi: 10.3390/plants12040859. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Breast Cancer. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: Mar 26, 2021.
-
- DeSantis C.E., Bray F., Ferlay J., Lortet-Tieulent J., Anderson B.O., Jemal A. International Variation in Female Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality Rates. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2015;24:1495–1506. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-15-0535. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- FAPEMIG CBB - APQ-03277-16, CBB APQ 01781-17/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais
- CNPq 454916/2014-0, 402653/2018-1, 168640/2018-0, CNPq 304337/2019-6/Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico
- PRINT 88887.581726/2020-00/Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
- Process99999.008121/2014-01/Alexander von Humboldt-Stiftung
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

