NF-κB and Pancreatic Cancer; Chapter and Verse
- PMID: 34572737
- PMCID: PMC8469693
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13184510
NF-κB and Pancreatic Cancer; Chapter and Verse
Abstract
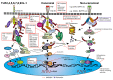
Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is one of the world's most lethal cancers. An increase in occurrence, coupled with, presently limited treatment options, necessitates the pursuit of new therapeutic approaches. Many human cancers, including PDAC are initiated by unresolved inflammation. The transcription factor NF-κB coordinates many signals that drive cellular activation and proliferation during immunity but also those involved in inflammation and autophagy which may instigate tumorigenesis. It is not surprising therefore, that activation of canonical and non-canonical NF-κB pathways is increasingly recognized as an important driver of pancreatic injury, progression to tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Paradoxically, NF-κB dysregulation has also been shown to inhibit pancreatic inflammation and pancreatic cancer, depending on the context. A pro-oncogenic or pro-suppressive role for individual components of the NF-κB pathway appears to be cell type, microenvironment and even stage dependent. This review provides an outline of NF-κB signaling, focusing on the role of the various NF-κB family members in the evolving inflammatory PDAC microenvironment. Finally, we discuss pharmacological control of NF-κB to curb inflammation, focussing on novel anti-cancer agents which reinstate the process of cancer cell death, the Smac mimetics and their pre-clinical and early clinical trials.
Keywords: NF-κB; PDAC; Smac mimetics; inflammation; pancreatic cancer; pancreatitis; therapy; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NF-κB/Rel Transcription Factors in Pancreatic Cancer: Focusing on RelA, c-Rel, and RelB.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jul 4;11(7):937. doi: 10.3390/cancers11070937. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31277415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the Role of Innate Immune NF-ĸB Pathway in Pancreatic Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 19;12(9):2675. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092675. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32961746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancement of NF-κB Signaling Pathway: A Novel Target in Pancreatic Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 5;19(12):3890. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123890. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30563089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The therapeutic targeting of the FGFR1/Src/NF-κB signaling axis inhibits pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma stemness and oncogenicity.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2018 Oct;35(7):663-677. doi: 10.1007/s10585-018-9919-5. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2018. PMID: 29987671
-
Hyper-O-GlcNAcylation is anti-apoptotic and maintains constitutive NF-κB activity in pancreatic cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 24;288(21):15121-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.470047. Epub 2013 Apr 16. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23592772 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enhancing chemosensitivity of PANC1 pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine using ANGTPL4, Notch1 and NF-κβ1 siRNAs.Future Sci OA. 2024 May 20;10(1):FSO918. doi: 10.2144/fsoa-2023-0145. eCollection 2024. Future Sci OA. 2024. PMID: 38817387 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of pancreatic cancer according to glycemic status in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a nationwide cohort study.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23308. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05868-3. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40603379 Free PMC article.
-
From silico to benchtop: cosmosiin as a PD-1/PDL-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor revealed through DFT, network pharmacology analysis, and molecular docking integrated experimental verification.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 2;15(28):22285-22310. doi: 10.1039/d5ra03831f. eCollection 2025 Jun 30. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40606194 Free PMC article.
-
The Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Neither Hot nor Cold.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 31;14(17):4236. doi: 10.3390/cancers14174236. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36077772 Free PMC article.
-
Breaking the oncogenic link: BCL10-MALT1 disruption as a precision strike against NF-κB-driven lymphomas.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 19;42(8):350. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02897-w. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40684038 Review.
References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer Global Cancer Observatory. [(accessed on 28 June 2019)]. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

