Laparoscopic Compared with Open D2 Gastrectomy on Perioperative and Long-Term, Stage-Stratified Oncological Outcomes for Gastric Cancer: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis of the IMIGASTRIC Database
- PMID: 34572753
- PMCID: PMC8465518
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13184526
Laparoscopic Compared with Open D2 Gastrectomy on Perioperative and Long-Term, Stage-Stratified Oncological Outcomes for Gastric Cancer: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis of the IMIGASTRIC Database
Abstract
Background: The laparoscopic approach in gastric cancer surgery is being increasingly adopted worldwide. However, studies focusing specifically on laparoscopic gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy are still lacking in the literature. This retrospective study aimed to compare the short-term and long-term outcomes of laparoscopic versus open gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy for gastric cancer.
Methods: The protocol-based, international IMIGASTRIC (International study group on Minimally Invasive surgery for Gastric Cancer) registry was queried to retrieve data on patients undergoing laparoscopic or open gastrectomy with D2 lymphadenectomy for gastric cancer with curative intent from January 2000 to December 2014. Eleven predefined, demographical, clinical, and pathological variables were used to conduct a 1:1 propensity score matching (PSM) analysis to investigate intraoperative and recovery outcomes, complications, pathological findings, and survival data between the two groups. Predictive factors of long-term survival were also assessed.
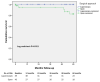
Results: A total of 3033 patients from 14 participating institutions were selected from the IMIGASTRIC database. After 1:1 PSM, a total of 1248 patients, 624 in the laparoscopic group and 624 in the open group, were matched and included in the final analysis. The total operative time (median 180 versus 240 min, p < 0.0001) and the length of the postoperative hospital stay (median 10 versus 14.8 days, p < 0.0001) were longer in the open group than in the laparoscopic group. The conversion to open rate was 1.9%. The proportion of patients with in-hospital complications was higher in the open group (21.3% versus 15.1%, p = 0.004). The median number of harvested lymph nodes was higher in the laparoscopic approach (median 32 versus 28, p < 0.0001), and the proportion of positive resection margins was higher (p = 0.021) in the open group (5.9%) than in the laparoscopic group (3.2%). There was no significant difference between the groups in five-year overall survival rates (77.4% laparoscopic versus 75.2% open, p = 0.229).
Conclusion: The adoption of the laparoscopic approach for gastric resection with D2 lymphadenectomy shortened the length of hospital stay and reduced postoperative complications with respect to the open approach. The five-year overall survival rate after laparoscopy was comparable to that for patients who underwent open D2 resection. The types of surgical approaches are not independent predictive factors for five-year overall survival.
Keywords: gastric cancer; laparoscopy; minimally invasive surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kitano S., Iso Y., Moriyama M., Sugimachi K. Laparoscopy-assisted Billroth I gastrectomy. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. 1994;4:146–148. - PubMed
-
- Inaki N., Etoh T., Ohyama T., Uchiyama K., Katada N., Koeda K., Yoshida K., Takagane A., Kojima K., Sakuramoto S., et al. A Multi-institutional, Prospective, Phase II Feasibility Study of Laparoscopy-Assisted Distal Gastrectomy with D2 Lymph Node Dissection for Locally Advanced Gastric Cancer (JLSSG0901) World J. Surg. 2015;39:2734–2741. doi: 10.1007/s00268-015-3160-z. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous