Microbial Biosurfactant: A New Frontier for Sustainable Agriculture and Pharmaceutical Industries
- PMID: 34573103
- PMCID: PMC8469275
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10091472
Microbial Biosurfactant: A New Frontier for Sustainable Agriculture and Pharmaceutical Industries
Abstract
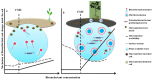
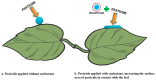
In the current scenario of changing climatic conditions and the rising global population, there is an urgent need to explore novel, efficient, and economical natural products for the benefit of humankind. Biosurfactants are one of the latest explored microbial synthesized biomolecules that have been used in numerous fields, including agriculture, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food processing, and environment-cleaning industries, as a source of raw materials, for the lubrication, wetting, foaming, emulsions formulations, and as stabilizing dispersions. The amphiphilic nature of biosurfactants have shown to be a great advantage, distributing themselves into two immiscible surfaces by reducing the interfacial surface tension and increasing the solubility of hydrophobic compounds. Furthermore, their eco-friendly nature, low or even no toxic nature, durability at higher temperatures, and ability to withstand a wide range of pH fluctuations make microbial surfactants preferable compared to their chemical counterparts. Additionally, biosurfactants can obviate the oxidation flow by eliciting antioxidant properties, antimicrobial and anticancer activities, and drug delivery systems, further broadening their applicability in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Nowadays, biosurfactants have been broadly utilized to improve the soil quality by improving the concentration of trace elements and have either been mixed with pesticides or applied singly on the plant surfaces for plant disease management. In the present review, we summarize the latest research on microbial synthesized biosurfactant compounds, the limiting factors of biosurfactant production, their application in improving soil quality and plant disease management, and their use as antioxidant or antimicrobial compounds in the pharmaceutical industries.
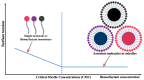
Keywords: antioxidant; biosurfactants; critical micelle concentration (C.M.C.); microorganism; plant disease management; soil quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microbially derived surfactants: an ecofriendly, innovative, and effective approach for managing environmental contaminants.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 26;12:1398210. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1398210. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39253704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosurfactants in agriculture.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Feb;97(3):1005-16. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4641-8. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23280539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosurfactants: A review of different strategies for economical production, their applications and recent advancements.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2025 Mar;337:103389. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2024.103389. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2025. PMID: 39765093 Review.
-
Microbial originated surfactants with multiple applications: a comprehensive review.Arch Microbiol. 2022 Jul 4;204(8):452. doi: 10.1007/s00203-022-03086-3. Arch Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35786779 Review.
-
Microbial Biosurfactant as an Alternate to Chemical Surfactants for Application in Cosmetics Industries in Personal and Skin Care Products: A Critical Review.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Apr 13;2023:2375223. doi: 10.1155/2023/2375223. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37090190 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Promising Application, Efficient Production, and Genetic Basis of Mannosylerythritol Lipids.Biomolecules. 2024 May 5;14(5):557. doi: 10.3390/biom14050557. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38785964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the antimicrobial and antibiofilm potential of biosurfactant produced by newly isolated Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strain 1625.Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 10;15:1459388. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1459388. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39318434 Free PMC article.
-
Biosurfactant Production by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens C11 and Streptomyces lavendulae C27 Isolated from a Biopurification System for Environmental Applications.Microorganisms. 2022 Sep 23;10(10):1892. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10101892. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296169 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Partition of Lipopeptides from Fermentation Broth: A Green and Sustainable Approach.ACS Omega. 2022 Dec 9;7(50):46646-46652. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c05587. eCollection 2022 Dec 20. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36570225 Free PMC article.
-
Tapping the Role of Microbial Biosurfactants in Pesticide Remediation: An Eco-Friendly Approach for Environmental Sustainability.Front Microbiol. 2021 Dec 23;12:791723. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.791723. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 35003022 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Popp J., Pető K., Nagy J. Pesticide productivity and food security: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013;33:243–255. doi: 10.1007/s13593-012-0105-x. - DOI
-
- Muthusamy K., Gopalakrishnan S., Ravi T.K., Sivachidambaram P. Biosurfactants: Properties, commercial production and application. Curr. Sci. 2008;94:736–747.
-
- Singh S.K., Singh M.K., Verma H., Singh P.P., Singh A.V., Rashmi K., Kumar A. Microbe Mediated Remediation of Environmental Contaminants. Woodhead Publishing; Sawston, UK: 2021. Biosurfactant producing microbes for clean-up of soil contaminants; pp. 89–93.
-
- Rahman P.K., Gakpe E. Production, characterisation and applications of biosurfactants-Review. Biotechnology. 2008;7:360–370. doi: 10.3923/biotech.2008.360.370. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

