Diosmetin Ameliorates Vascular Dysfunction and Remodeling by Modulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and p-JNK/p-NF-κB Expression in Hypertensive Rats
- PMID: 34573119
- PMCID: PMC8469706
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox10091487
Diosmetin Ameliorates Vascular Dysfunction and Remodeling by Modulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and p-JNK/p-NF-κB Expression in Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
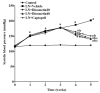
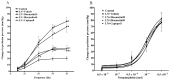
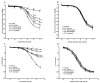
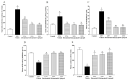
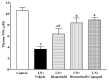
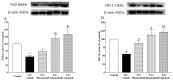
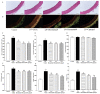
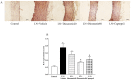
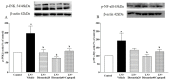
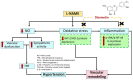
Diosmetin is a citrus flavonoid that has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. This study examined the effect of diosmetin on blood pressure and vascular alterations and its underlying mechanisms in experimentally hypertensive rats. Male Sprague rats were administered Nω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester L-NAME for five weeks and were given diosmetin at doses of 20 or 40 mg/kg or captopril (5 mg/kg) for two weeks. Diosmetin alleviated hypertension, improved endothelial dysfunction, and suppressed the overactivity of sympathetic nerve-mediated vasoconstriction in aorta and mesentery hypertensive rats (p < 0.05). Increases in plasma and aortic tissue malondialdehyde (MDA) and carotid superoxide generations and reductions of plasma superoxide dismutase, catalase, and nitric oxide in hypertensive rats were ameliorated by diosmetin (p < 0.05). Diosmetin increased the protein expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in hypertensive rats. Furthermore, diosmetin mitigated hypertrophy and collagen accumulation of the aortic wall in L-NAME rats. It exhibited an anti-inflammatory effect by reducing interleukin-6 (IL-6) accumulation and by overexpressing the phospho-c-Jun N-terminal kinases (p-JNK) and the phospho-nuclear factor-kappaB (p-NF-κB) proteins in the aorta (p < 0.05). Captopril was a positive control substance and had similar effects to diosmetin. In summary, diosmetin reduced blood pressure and alleviated vascular abnormalities in L-NAME-treated rats. These effects might be related to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects as well as to the modulation of the expression of the Nrf2/HO1 and p-JNK/NF-κB proteins.
Keywords: diosmetin; inflammation; oxidative stress; vascular function; vascular remodeling.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

