MED12 Mutation in Two Families with X-Linked Ohdo Syndrome
- PMID: 34573309
- PMCID: PMC8471817
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12091328
MED12 Mutation in Two Families with X-Linked Ohdo Syndrome
Abstract
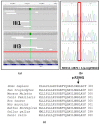
X-linked intellectual deficiency (XLID) is a widely heterogeneous group of genetic disorders that involves more than 100 genes. The mediator of RNA polymerase II subunit 12 (MED12) is involved in the regulation of the majority of RNA polymerase II-dependent genes and has been shown to cause several forms of XLID, including Opitz-Kaveggia syndrome also known as FG syndrome (MIM #305450), Lujan-Fryns syndrome (MIM #309520) and the X-linked Ohdo syndrome (MIM #300895). Here, we report on two first cousins with X-linked Ohdo syndrome with a missense mutation in MED12 gene, identified through whole exome sequencing. The probands had facial features typical of X-linked Ohdo syndrome, including blepharophimosis, ptosis, a round face with a characteristic nose and a narrow mouth. Nextera DNA Exome kit (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) was used for exome capture. The variant identified was a c.887G > A substitution in exon 7 of the MED12 gene leading to the substitution of a glutamine for a highly conserved arginine (p. Arg296Gln). Although the variant described has been previously reported in the literature, our study contributes to the expanding phenotypic spectrum of MED12-related disorders and above all, it demonstrates the phenotypic variability among different affected patients despite harboring identical mutations.
Keywords: MED12; X-linked intellectual deficiency; genotype-phenotype correlation; next generation sequencing (NGS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Rubinato E., Rondeau S., Giuliano F., Kossorotoff M., Parodi M., Gherbi S., Steffan J., Jonard L., Marlin S. MED12 Missense Mutation in a Three-Generation Family. Clinical Characterization of MED12-Related Disorders and Literature Review. Eur. J. Med Genet. 2020;63:103768. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2019.103768. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li D., Strong A., Shen K.M., Cassiman D., Van Dyck M., Linhares N.D., Valadares E.R., Wang T., Pena S.D.J., Jaeken J., et al. De Novo Loss-of-Function Variants in X-Linked MED12 Are Associated with Hardikar Syndrome in Females. Genet. Med. 2021;23:637–644. doi: 10.1038/s41436-020-01031-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Polla D.L., Bhoj E.J., Verheij J.B.G.M., Wassink-Ruiter J.S.K., Reis A., Deshpande C., Gregor A., Hill-Karfe K., Silfhout A.T.V., Pfundt R., et al. De Novo Variants in MED12 Cause X-Linked Syndromic Neurodevelopmental Disorders in 18 Females. Genet. Med. 2021;23:645–652. doi: 10.1038/s41436-020-01040-6. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

