SIRT7 Acts as a Guardian of Cellular Integrity by Controlling Nucleolar and Extra-Nucleolar Functions
- PMID: 34573343
- PMCID: PMC8467518
- DOI: 10.3390/genes12091361
SIRT7 Acts as a Guardian of Cellular Integrity by Controlling Nucleolar and Extra-Nucleolar Functions
Abstract
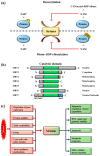
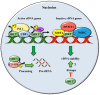
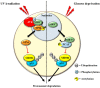
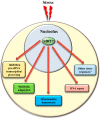
Sirtuins are key players for maintaining cellular homeostasis and are often deregulated in different human diseases. SIRT7 is the only member of mammalian sirtuins that principally resides in the nucleolus, a nuclear compartment involved in ribosomal biogenesis, senescence, and cellular stress responses. The ablation of SIRT7 induces global genomic instability, premature ageing, metabolic dysfunctions, and reduced stress tolerance, highlighting its critical role in counteracting ageing-associated processes. In this review, we describe the molecular mechanisms employed by SIRT7 to ensure cellular and organismal integrity with particular emphasis on SIRT7-dependent regulation of nucleolar functions.
Keywords: SIRT7; deacetylation; nucleolus; sirtuins; stress responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Simonet N.G., Thackray J.K., Vazquez B.N., Ianni A., Espinosa-Alcantud M., Morales-Sanfrutos J., Hurtado-Bagès S., Sabidó E., Buschbeck M., Tischfield J., et al. SirT7 auto-ADP-ribosylation regulates glucose starvation response through mH2A1. Sci. Adv. 2020;6:eaaz2590. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz2590. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

