Neuropathic Pain and Ultrasonography: A Multiperspective Literature Evaluation
- PMID: 34574046
- PMCID: PMC8470278
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11091705
Neuropathic Pain and Ultrasonography: A Multiperspective Literature Evaluation
Abstract
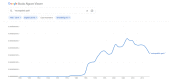
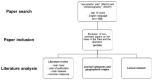
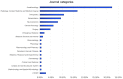
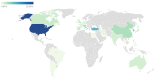
Among the tools useful for the management of neuropathic pain, ultrasound presents several advantages, shown by the literature. We assessed the scientific production about neuropathic pain and ultrasound from different points of view: general topics, journal categories, geographical origin and lexical analysis. We searched papers on PubMed using the Medical Subject Headings "neuropathic pain" AND "ultrasound". We collected data about the journals where the papers were published, the country of the affiliation of the first author. For the lexical analysis, we evaluated the presence of selected words in the papers, and we built a graph representing the connections among words and papers. The papers were focused on the use of ultrasound as a diagnostic tool and guide for the therapy, assessing its application in different diseases such as Morton's neuroma and piriformis syndrome. The most represented journal category was anesthesia while the most common country the United States of America. The lexical analysis confirmed the importance of ultrasound for diagnosis of specific disease and treatment of pain. The described approaches provide a multiperspective evaluation of the literature and may support the interpretation of the information contained by the papers.
Keywords: diagnosis; graph-theory; pain; rehabilitation; treatment; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

