Effects of a Mixed Limosilactobacillus fermentum Formulation with Claimed Probiotic Properties on Cardiometabolic Variables, Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Male Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet
- PMID: 34574313
- PMCID: PMC8471400
- DOI: 10.3390/foods10092202
Effects of a Mixed Limosilactobacillus fermentum Formulation with Claimed Probiotic Properties on Cardiometabolic Variables, Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Male Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet
Abstract
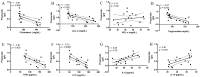
High-fat diet (HFD) consumption has been linked to dyslipidemia, low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress. This study investigated the effects of a mixed formulation with Limosilactobacillusfermentum 139, L. fermentum 263 and L. fermentum 296 on cardiometabolic parameters, fecal short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) contents and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in colon and heart tissues of male rats fed an HFD. Male Wistar rats were grouped into control diet (CTL, n = 6), HFD (n = 6) and HFD with L. fermentum formulation (HFD-Lf, n = 6) groups. The L.fermentum formulation (1 × 109 CFU/mL of each strain) was administered twice a day for 4 weeks. After a 4-week follow-up, biochemical parameters, fecal SCFA, cytokines and oxidative stress variables were evaluated. HFD consumption caused hyperlipidemia, hyperglycemia, low-grade inflammation, reduced fecal acetate and propionate contents and increased biomarkers of oxidative stress in colon and heart tissues when compared to the CTL group. Rats receiving the L. fermentum formulation had reduced hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia, but similar SCFA contents in comparison with the HFD group (p < 0.05). Rats receiving the L. fermentum formulation had increased antioxidant capacity throughout the colon and heart tissues when compared with the control group. Administration of a mixed L. fermentum formulation prevented hyperlipidemia, inflammation and oxidative stress in colon and heart tissues induced by HFD consumption.
Keywords: Limosilactobacillus fermentum; high-fat diet; inflammation; oxidative stress; probiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

