Obesity and Thyroid Axis
- PMID: 34574358
- PMCID: PMC8467528
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18189434
Obesity and Thyroid Axis
Abstract
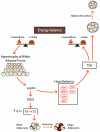
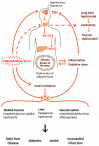
Development of obesity is primarily the result of imbalance between energy intake and energy expenditure. Thyroid hormones influence energy expenditure by regulating cellular respiration and thermogenesis and by determining resting metabolic rate. Triiodothyronine influences lipid turnover in adipocytes and impacts appetite regulation through the central nervous system, mainly the hypothalamus. Thyroid-stimulating hormone may also influence thermogenesis, suppress appetite and regulate lipid storage through lipolysis and lipogenesis control. Subclinical hypothyroidism may induce changes in basal metabolic rate with subsequent increase in BMI, but obesity can also affect thyroid function via several mechanisms such as lipotoxicity and changes in adipokines and inflammatory cytokine secretion. The present study investigated the complex and mutual relationships between the thyroid axis and adiposity.
Keywords: TSH; adipokines; adipose tissue; obesity; thyroid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pasquali R., Casanueva F., Haluzik M., van Hulsteijn L., Ledoux S., Monteiro M.P., Salvador J., Santini F., Toplak H., Dekkers O.M. European Society of Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline: Endocrine work-up in obesity. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020;182:G1–G32. doi: 10.1530/EJE-19-0893. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abdi H., Faam B., Gharibzadeh S., Mehran L., Tohidi M., Azizi F., Amouzegar A. Determination of age and sex specific TSH and FT4 reference limits in overweight and obese individuals in an iodine-replete region: Tehran Thyroid Study (TTS) Endocr. Res. 2021;46:37–43. doi: 10.1080/07435800.2020.1854778. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Santini F., Marzullo P., Rotondi M., Ceccarini G., Pagano L., Ippolito S., Chiovato L., Biondi B. Mechanisms in endocrinology: The crosstalk between thyroid gland and adipose tissue: Signal integration in health and disease. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014;171:137–152. doi: 10.1530/EJE-14-0067. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

