Factors Associated with Burden in Caregivers of Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease (A Systematic Review)
- PMID: 34574986
- PMCID: PMC8468425
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare9091212
Factors Associated with Burden in Caregivers of Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease (A Systematic Review)
Abstract
Background: Caring for a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) is highly stressful and can impact negatively on the physical and psychological well-being of caregivers. To accurately assess caregiver burden (CB), health care providers (HCPs) need to identify characteristics associated with an increase in CB.
Aim: The aim of this review is to explore CB in caregivers of adult patients with ESKD and to identify characteristics associated with any increase in CB.
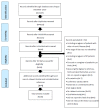
Method: A comprehensive literature search was completed using five electronic databases. Medline, Embase, CINHAL, PsycINFO, and Scopus. The Joanna Briggs Institute checklist (JBI) was used to quality appraise full text papers included in the review. No time limit for the date of publication of studies was employed, to enable the inclusion of more extensive literature.
Results: A total of 38 relevant studies from 18 countries were identified and included in the review. A variety of patient and caregiver factors can impact positively or negatively on CB, including socio-demographic factors of patients and caregivers, disease-related factors, situational and relational factors, environmental factors, and psychological factors.
Conclusion: This review provides awareness to HCPs of the important factors associated with CB, when assessing or targeting interventions for caregivers experiencing burden.
Keywords: caregiver burden; caregiver strain; caregiver stress; end-stage kidney disease; renal failure; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Similar articles
-
Factors affecting caregiver burden of terminally ill adults in the home setting - A systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2011;9(45):1883-1916. doi: 10.11124/01938924-201109450-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 27820549
-
Effectiveness of interventions that assist caregivers to support people with dementia living in the community: a systematic review.Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2008 Jun;6(2):137-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-1609.2008.00090.x. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2008. PMID: 21631819
-
Effectiveness of interventions that assist caregivers to support people with dementia living in the community: a systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2008;6(13):484-544. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200806130-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 27820474
-
Health Education Programmes to Improve Foot Self-Care Knowledge and Behaviour among Older People with End-Stage Kidney Disease (ESKD) Receiving Haemodialysis (A Systematic Review).Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jun 20;10(6):1143. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10061143. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35742194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caregiver burden among dementia patient caregivers: a review of the literature.J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2008 Aug;20(8):423-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-7599.2008.00342.x. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 2008. PMID: 18786017 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Implementers' Perspectives on the Development and Implementation of an e-Mental Health Intervention for Caregivers of Adults With Chronic Kidney Disease: Qualitative Interview Study.JMIR Hum Factors. 2023 Nov 17;10:e51461. doi: 10.2196/51461. JMIR Hum Factors. 2023. PMID: 37792676 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing Burden, Anxiety, Depression, and Quality of Life among Caregivers of Hemodialysis Patients in Indonesia: A Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 9;19(8):4544. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19084544. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35457412 Free PMC article.
-
Study of Caregiver Burden in Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis.Indian J Nephrol. 2024 Nov-Dec;34(6):597-602. doi: 10.25259/ijn_424_23. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Indian J Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39649306 Free PMC article.
-
The mediating effect of family resilience between coping styles and caregiver burden in maintenance hemodialysis patients: a cross-sectional study.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Mar 5;25(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03520-2. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38443869 Free PMC article.
-
Narrative Review: Clinical Implications and Assessment of Frailty in Patients With Advanced CKD.Kidney Int Rep. 2023 Dec 30;9(4):791-806. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2023.12.022. eCollection 2024 Apr. Kidney Int Rep. 2023. PMID: 38765572 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources