Renal Outcome of IgM Nephropathy: A Comparative Prospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 34575298
- PMCID: PMC8466757
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10184191
Renal Outcome of IgM Nephropathy: A Comparative Prospective Cohort Study
Abstract
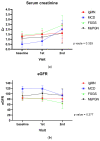
Immunoglobulin M nephropathy (IgMN) is an idiopathic glomerulonephritis characterized by diffuse deposits of IgM in the glomerular mesangium. However, its renal prognosis remains unknown. We compared renal outcomes of IgMN patients with those of patients with minimal change disease (MCD), focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), or mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis (MsPGN) from a prospective observational cohort, with 1791 patients undergoing native kidney biopsy in eight hospitals affiliated with The Catholic University of Korea between December 2014 and October 2020. IgMN had more mesangial proliferation and matrix expansion than MsPGN and more tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis than MCD. IgMN patients had decreased eGFR than MCD patients in the earlier follow-up. However, there was no significant difference in urine protein or eGFR among all patients at the last follow-up. When IgMN was divided into three subtypes, patients with FSGS-like IgMN tended to have lower eGFR than those with MCD-like or MsPGN-like IgMN but higher proteinuria than MsPGN-like IgMN without showing a significant difference. The presence of hypertension at the time of kidney biopsy predicted ≥20% decline of eGFR over two years in IgMN patients. Our data indicate that IgMN would have a clinical course and renal prognosis similar to MCD, FSGS, and MsPGN.
Keywords: IgM nephropathy; glomerulonephritis; kidney biopsy; prognosis; renal outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

