The Role of Neuropeptides in Pathogenesis of Dry Dye
- PMID: 34575359
- PMCID: PMC8471988
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10184248
The Role of Neuropeptides in Pathogenesis of Dry Dye
Abstract
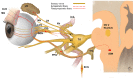
Neuropeptides are known as important mediators between the nervous and immune systems. Recently, the role of the corneal nerve in the pathogenesis of various ocular surface diseases, including dry eye disease, has been highlighted. Neuropeptides are thought to be important factors in the pathogenesis of dry eye disease, as suggested by the well-known role between the nervous and immune systems, and several recently published studies have elucidated the previously unknown pathogenic mechanisms involved in the role of the neuropeptides secreted from the corneal nerves in dry eye disease. Here, we reviewed the emerging concept of neurogenic inflammation as one of the pathogenic mechanisms of dry eye disease, the recent results of related studies, and the direction of future research.
Keywords: calcitonin gene-related peptide; corneal nerve; dry eye; neurogenic inflammation; neuropeptide; neuropeptide Y; pathogenesis; substance P; vasoactive intestinal peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

