Black Phosphorus, an Emerging Versatile Nanoplatform for Cancer Immunotherapy
- PMID: 34575419
- PMCID: PMC8466662
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091344
Black Phosphorus, an Emerging Versatile Nanoplatform for Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
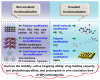
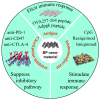
Black phosphorus (BP) is one of the emerging versatile nanomaterials with outstanding biocompatibility and biodegradability, exhibiting great potential as a promising inorganic nanomaterial in the biomedical field. BP nanomaterials possess excellent ability for valid bio-conjugation and molecular loading in anticancer therapy. Generally, BP nanomaterials can be classified into BP nanosheets (BPNSs) and BP quantum dots (BPQDs), both of which can be synthesized through various preparation routes. In addition, BP nanomaterials can be applied as photothermal agents (PTA) for the photothermal therapy (PTT) due to their high photothermal conversion efficiency and larger extinction coefficients. The generated local hyperpyrexia leads to thermal elimination of tumor. Besides, BP nanomaterials are capable of producing singlet oxygen, which enable its application as a photosensitizer for photodynamic therapy (PDT). Moreover, BP nanomaterials can be oxidized and degraded to nontoxic phosphonates and phosphate under physiological conditions, improving their safety as a nano drug carrier in cancer therapy. Recently, it has been reported that BP-based PTT is capable of activating immune responses and alleviating the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment by detection of T lymphocytes and various immunocytokines, indicating that BP-based nanocomposites not only serve as effective PTAs to ablate large solid tumors but also function as an immunomodulation agent to eliminate discrete tumorlets. Therefore, BP-mediated immunotherapy would provide more possibilities for synergistic cancer treatment.
Keywords: black phosphorus nanomaterial; cancer immunotherapy; immune stimulation; photodynamic therapy; photothermal therapy; synergistic therapeutic modality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 31872756 and 32071387/National Nature Science Foundation of China
- 2016ZX09101031/National Major Scientific and Technological Special Project for 'Significant New Drugs Development'
- JY-079/Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province
- 2020KTSCX259/Characteristic Innovative Project of Guandong Province Ordinary Institution of Higher Education
- 2019-rbcxjj-005/Clinical Research Innovation Training Project of Baoshan Branch of Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

