Spontaneously Self-Assembled Microgel Film as Co-Delivery System for Skincare Applications
- PMID: 34575498
- PMCID: PMC8472779
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091422
Spontaneously Self-Assembled Microgel Film as Co-Delivery System for Skincare Applications
Abstract
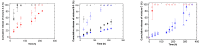
Nowadays, the design of innovative delivery systems is driving new product developments in the field of skincare. In this regard, serving as potential candidates for on-demand drug delivery and fulfilling advanced mechanical and optical properties together with surface protection, spontaneously self-assembled microgel films can be proposed as ideal smart skincare systems. Currently, the high encapsulation of more than one drug simultaneously in a film is a very challenging task. Herein, different ratios (1:1, 3:1, 9:1) of different mixtures of hydrophilic/hydrophobic UVA/UVB-absorbers working together in synergy and used for skin protection were encapsulated efficiently into spontaneously self-assembled microgel films. In addition, in vitro release profiles show a controlled release of the different active molecules regulated by the pH and temperature of the medium. The analysis of the release mechanisms by the Peppas-Sahlin model indicated a superposition of diffusion-controlled and swelling-controlled releases. Finally, the distribution of active molecule mixtures into the film was studied by confocal Raman microscopy imaging corroborating the release profiles obtained.
Keywords: co-delivery; cosmetic active molecules; self-assembled microgel film.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pérez-Guzmán C.J., Castro-Muñoz R. A Review of Zein as Potential Biopolymer for Tissue Engineering and Nanotechnological Applications. Processes. 2020;8:1376. doi: 10.3390/pr8111376. - DOI
-
- Biswal T. Biopolymers for tissue engineering applications: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021;41:397–402. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.628. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

