siRNA-Loaded Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles for KRAS Gene Silencing in Anti-Pancreatic Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 34575504
- PMCID: PMC8466089
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091428
siRNA-Loaded Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles for KRAS Gene Silencing in Anti-Pancreatic Cancer Therapy
Abstract
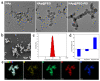
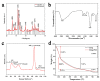
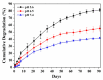
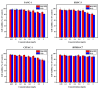
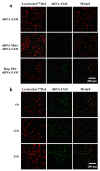
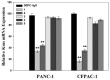
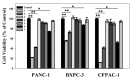
Pancreatic carcinoma (PC) is greatly induced by the KRAS gene mutation, but effective targeted delivery for gene therapy has not existed. Small interfering ribonucleic acid (siRNA) serves as an advanced therapeutic modality and holds great promise for cancer treatment. However, the development of a non-toxic and high-efficiency carrier system to accurately deliver siRNA into cells for siRNA-targeted gene silencing is still a prodigious challenge. Herein, polyethylenimine (PEI)-modified hydroxyapatite (HAp) nanoparticles (HAp-PEI) were fabricated. The siRNA of the KRAS gene (siKras) was loaded onto the surface of HAp-PEI via electrostatic interaction between siRNA and PEI to design the functionalized HAp-PEI nanoparticle (HAp-PEI/siKras). The HAp-PEI/siKras was internalized into the human PC cells PANC-1 to achieve the maximum transfection efficiency for active tumor targeting. HAp-PEI/siKras effectively knocked down the expression of the KRAS gene and downregulated the expression of the Kras protein in vitro. Furthermore, the treatment with HAp-PEI/siKras resulted in greater anti-PC cells' (PANC-1, BXPC-3, and CFPAC-1) efficacy in vitro. Additionally, the HAp-PEI exhibited no obvious in vitro cytotoxicity in normal pancreatic HPDE6-C7 cells. These findings provided a promising alternative for the therapeutic route of siRNA-targeted gene engineering for anti-pancreatic cancer therapy.
Keywords: KRAS gene; anticancer; gene silence; hydroxyapatite; pancreatic cancer cells; siRNA delivery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeted nanodelivery of siRNA against KRAS G12D inhibits pancreatic cancer.Acta Biomater. 2023 Sep 15;168:529-539. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2023.07.008. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Acta Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37451658
-
siRNA-loaded selenium nanoparticle modified with hyaluronic acid for enhanced hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Mar 15;13:1539-1552. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S157519. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29588583 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of the efficacy of siRNA-mediated KRAS gene silencing in pancreatic cancer therapy.PeerJ. 2024 Nov 12;12:e18214. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18214. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39553720 Free PMC article.
-
Polyethylenimine as a promising vector for targeted siRNA delivery.Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2012 May;7(2):121-30. doi: 10.2174/157488412800228857. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22432843 Review.
-
Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles for Improved Cancer Theranostics.J Funct Biomater. 2022 Jul 20;13(3):100. doi: 10.3390/jfb13030100. J Funct Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35893468 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
pH-Responsive Drug Delivery Nanoplatforms as Smart Carriers of Unsymmetrical Bisacridines for Targeted Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 6;15(1):201. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010201. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36678830 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxyapatite-based carriers for tumor targeting therapy.RSC Adv. 2023 Jun 1;13(24):16512-16528. doi: 10.1039/d3ra01476b. eCollection 2023 May 30. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37274393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in nanohydroxyapatite: synthesis, biomedical applications and composite developments.Regen Biomater. 2024 Nov 5;12:rbae129. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbae129. eCollection 2025. Regen Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39776858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles Bounded to Interfering RNAs as a Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024 Nov-Dec;16(6):e2013. doi: 10.1002/wnan.2013. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39510122 Free PMC article.
-
Ion Doped Hollow Silica Nanoparticles as Promising Oligonucleotide Delivery Systems to Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Sep 20;19:9741-9755. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S461167. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39329032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tan X., Sivakumar S., Bednarsch J., Wiltberger G., Kather J.N., Niehues J., de Vos-Geelen J., Valkenburg-van Iersel L., Kintsler S., Roeth A. Nerve fibers in the tumor microenvironment in neurotropic cancer—pancreatic cancer and cholangiocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2021;40:899–908. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01578-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

