Mesoporous Calcium-Silicate Nanoparticles Loaded with Low-Dose Triton-100+Ag+ to Achieve Both Enhanced Antibacterial Properties and Low Cytotoxicity for Dentin Disinfection of Human Teeth
- PMID: 34575596
- PMCID: PMC8464954
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091518
Mesoporous Calcium-Silicate Nanoparticles Loaded with Low-Dose Triton-100+Ag+ to Achieve Both Enhanced Antibacterial Properties and Low Cytotoxicity for Dentin Disinfection of Human Teeth
Abstract
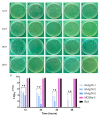
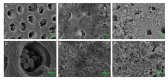
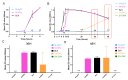
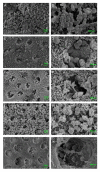
Mesoporous calcium-silicate nanoparticles (MCSNs) are excellent biomaterials for controlled drug delivery and mineralization induction. In this study, MCSNs were loaded with low-dose silver ion (Ag+) and Triton X-100 (TX-100) as the M-AgTX to achieve both enhanced antibacterial properties and low cytotoxicity for dentin disinfection. The physicochemical property, biocompatibility, infiltration ability into dentinal tubules, anti-bacterial ability against both planktonic Enterococcusfaecalis (E. faecalis) and its biofilm on dentin, effects on dentin microhardness and in vitro mineralization property were systematically investigated. Results confirmed that the MCSNs and M-AgTX nanoparticles showed typical morphology of mesoporous materials and exhibited sustained release of chemicals with an alkaline pH value over time. M-AgTX also exhibited excellent biocompatibility on MC3T3-E1 cells and could eliminate 100% planktonic E. faecalis after 48-h treatment. On dentin slices, it could enter dentinal tubules by ultrasonic activation and inhibit the growth of E. faecalis on dentin. M-AgTX could completely inactive 28-day E. faecalis biofilm. TEM confirmed the destruction of cell membrane integrity and Ag+ infiltration into bacteria by M-AgTX. Besides, dentin slices medicated with M-AgTX nanoparticles displayed an increased microhardness. After being immersed in SBF for 7 days, apatite crystals could be observed on the surface of the material tablets. M-AgTX could be developed into a new multifunctional intra-canal medication or bone defect filling material for infected bone defects due to its sustained release profile, low cytotoxicity, infiltration ability, enhanced anti-bacterial and mineralization features.
Keywords: Enterococcus faecalis; Triton X-100; mesoporous; nanoparticle; root canal disinfection; silver.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Carr G.B., Schwartz R.S., Schaudinn C., Gorur A., Costerton J.W. Ultrastructural examination of failed molar retreatment with secondary apical periodontitis: An examination of endodontic biofilms in an endodontic retreatment failure. J. Endod. 2009;35:1303–1309. doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2009.05.035. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

