The Role of Noninvasive Respiratory Management in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia
- PMID: 34575661
- PMCID: PMC8469068
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm11090884
The Role of Noninvasive Respiratory Management in Patients with Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia
Abstract
Acute hypoxemic respiratory failure is the principal cause of hospitalization, invasive mechanical ventilation and death in severe COVID-19 infection. Nearly half of intubated patients with COVID-19 eventually die. High-Flow Nasal Oxygen (HFNO) and Noninvasive Ventilation (NIV) constitute valuable tools to avert endotracheal intubation in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia who do not respond to conventional oxygen treatment. Sparing Intensive Care Unit beds and reducing intubation-related complications may save lives in the pandemic era. The main drawback of HFNO and/or NIV is intubation delay. Cautious selection of patients with severe hypoxemia due to COVID-19 disease, close monitoring and appropriate employment and titration of HFNO and/or NIV can increase the rate of success and eliminate the risk of intubation delay. At the same time, all precautions to protect the healthcare personnel from viral transmission should be taken. In this review, we summarize the evidence supporting the application of HFNO and NIV in severe COVID-19 hypoxemic respiratory failure, analyse the risks associated with their use and provide a path for their proper implementation.
Keywords: COVID-19; High Flow Nasal Oxygen; Noninvasive Ventilation; SARS-COV-2; noninvasive respiratory treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest in relation to the manuscript.
Figures
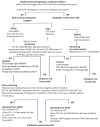
References
-
- Mauri T., Alban L., Turrini C., Cambiaghi B., Carlesso E., Taccone P., Bottino N., Lissoni A., Spadaro S., Volta C.A., et al. Optimum Support by High-Flow Nasal Cannula in Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure: Effects of Increasing Flow Rates. Intensive Care Med. 2017;43:1453–1463. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4890-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

