Enhanced Antiviral Function of Magnesium Chloride-Modified Heparin on a Broad Spectrum of Viruses
- PMID: 34576237
- PMCID: PMC8466540
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms221810075
Enhanced Antiviral Function of Magnesium Chloride-Modified Heparin on a Broad Spectrum of Viruses
Abstract
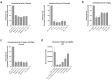
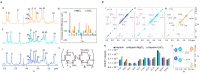
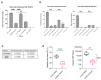
Previous studies reported on the broad-spectrum antiviral function of heparin. Here we investigated the antiviral function of magnesium-modified heparin and found that modified heparin displayed a significantly enhanced antiviral function against human adenovirus (HAdV) in immortalized and primary cells. Nuclear magnetic resonance analyses revealed a conformational change of heparin when complexed with magnesium. To broadly explore this discovery, we tested the antiviral function of modified heparin against herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and found that the replication of HSV-1 was even further decreased compared to aciclovir. Moreover, we investigated the antiviral effect against the new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and measured a 55-fold decreased viral load in the supernatant of infected cells associated with a 38-fold decrease in virus growth. The advantage of our modified heparin is an increased antiviral effect compared to regular heparin.
Keywords: HSV-1; NMR; SARS-CoV-2; adenovirus; antiviral; magnesium chloride; modified heparin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ghezzi S., Cooper L., Rubio A., Pagani I., Capobianchi M.R., Ippolito G., Pelletier J., Meneghetti M.C.Z., Lima M.A., Skidmore M.A. Heparin prevents Zika virus induced-cytopathic effects in human neural progenitor cells. Antivir. Res. 2017;140:13–17. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.12.023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

