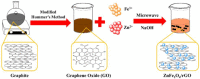
Facile Microwave Hydrothermal Synthesis of ZnFe2O4/rGO Nanocomposites and Their Ultra-Fast Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye
- PMID: 34576618
- PMCID: PMC8467475
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14185394
Facile Microwave Hydrothermal Synthesis of ZnFe2O4/rGO Nanocomposites and Their Ultra-Fast Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye
Abstract
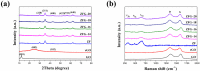
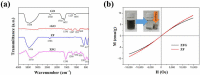
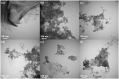
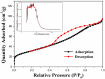
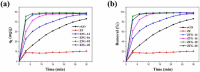
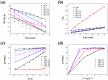
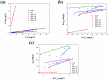
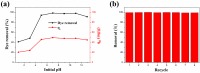
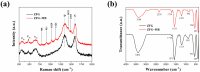
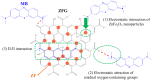
The industry development in the last 200 years has led to to environmental pollution. Dyes emitted by pharmaceutical and other industries are major organic pollutants. Organic dyes are a pollutant that must be removed from the environment. In this work, we adopt a facile microwave hydrothermal method to synthesize ZnFe2O4/rGO (ZFG) adsorbents and investigate the effect of synthesis temperature. The crystal structure, morphology, chemical state, and magnetic property of the nanocomposite are investigated by X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and a vibrating sample magnetometer. Furthermore, the synthesized ZFGs are used to remove methylene blue (MB) dye, and the adsorption kinetics, isotherm, mechanism, and reusability of this nanomaterial are studied. The optimal ZFG nanocomposite had a dye removal percentage of almost 100%. The fitting model of adsorption kinetics followed the pseudo-second-order model. The isotherm model followed the Langmuir isotherm and the theoretical maximum adsorption capacity of optimal ZFG calculated by this model was 212.77 mg/g. The π-π stacking and electrostatic interaction resulted in a high adsorption efficiency of ZFG for MB adsorption. In addition, this nanocomposite could be separated by a magnet and maintain its dye removal percentage at almost 100% removal after eight cycles, which indicates its high suitability for utilization in water treatment.
Keywords: ZnFe2O4/rGO; dye adsorption; microwave hydrothermal method.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synthesis and sonocatalytic performance of a ternary magnetic MIL-101(Cr)/RGO/ZnFe2O4 nanocomposite for degradation of dye pollutants.Ultrason Sonochem. 2018 Apr;42:647-658. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.12.033. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Ultrason Sonochem. 2018. PMID: 29429713
-
Three different methods for ZnO-RGO nanocomposite synthesis and its adsorption capacity for methylene blue dye removal in a comparative study.BMC Chem. 2025 Jan 18;19(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13065-025-01381-w. BMC Chem. 2025. PMID: 39827167 Free PMC article.
-
In Situ Synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) at the Surface of Fe3O4@AC as Highly Efficient Dye Adsorbing Nanocomposite.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 9;20(22):5612. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225612. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31717564 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of magnetic oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotube-κ-carrageenan-Fe3O4 nanocomposite adsorbent and its application in cationic Methylene Blue dye adsorption.Carbohydr Polym. 2016 Aug 20;147:79-88. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.03.099. Epub 2016 Apr 17. Carbohydr Polym. 2016. PMID: 27178911
-
Synthesis and characterization of magnetic clay-based carboxymethyl cellulose-acrylic acid hydrogel nanocomposite for methylene blue dye removal from aqueous solution.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Dec;27(35):44089-44105. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10166-8. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32761344
Cited by
-
One-Step Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of MnFe2O4/rGO Nanocomposites and Their Electrochemical Properties in Supercapacitors.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 27;10(5):4473-4485. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07810. eCollection 2025 Feb 11. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39959066 Free PMC article.
-
One-step preparation, characterization, and anticancer potential of ZnFe2O4/RGO nanocomposites.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Sep;31(9):101735. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.101735. Epub 2023 Aug 5. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 37638224 Free PMC article.
-
Activated Carbon/ZnFe2O4 Nanocomposite Adsorbent for Efficient Removal of Crystal Violet Cationic Dye from Aqueous Solutions.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Sep 16;12(18):3224. doi: 10.3390/nano12183224. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145011 Free PMC article.
-
A Facile Microwave Hydrothermal Synthesis of ZnFe2O4/rGO Nanocomposites for Supercapacitor Electrodes.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Mar 13;13(6):1034. doi: 10.3390/nano13061034. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36985927 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of MNPs/rGO/PMMA Composite for the Removal of Hazardous Cr(VI) from Tannery Wastewater through Batch and Continuous Mode Adsorption.Materials (Basel). 2021 Nov 16;14(22):6923. doi: 10.3390/ma14226923. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832323 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hussain S., Khan N., Gul S., Khan S., Khan H. Contamination of water resources by food dyes and its removal technologies. In: Eyvaz M., Yüksel E., editors. Water Chemistry. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2020. pp. 113–126.
-
- Derakhshan Z., Baghapour M.A., Ranjbar M., Faramarzian M. Adsorption of methylene blue dye from aqueous solutions by modified pumice stone: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. Health Scope. 2013;2:136–144. doi: 10.17795/jhealthscope-12492. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

