Antimicrobial Resistance and Comparative Genome Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Isolated in Egypt
- PMID: 34576775
- PMCID: PMC8465295
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9091880
Antimicrobial Resistance and Comparative Genome Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Isolated in Egypt
Abstract
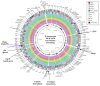
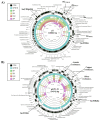
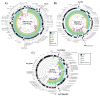
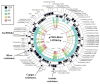
Klebsiella pneumoniae is an important human pathogen in both developing and industrialised countries that can causes a variety of human infections, such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections and bacteremia. Like many Gram-negative bacteria, it is becoming resistant to many frontline antibiotics, such as carbapenem and cephalosporin antibiotics. In Egypt, K. pneumoniae is increasingly recognised as an emerging pathogen, with high levels of antibiotic resistance. However, few Egyptian K. pneumoniae strains have been sequenced and characterised. Hence, here, we present the genome sequence of a multidrug resistant K. pneumoniae strain, KPE16, which was isolated from a child in Assiut, Egypt. We report that it carries multiple antimicrobial resistance genes, including a blaNDM-1 carbapenemase and extended spectrum β-lactamase genes (i.e., blaSHV-40, blaTEM-1B, blaOXA-9 and blaCTX-M-15). By comparing this strain with other Egyptian isolates, we identified common plasmids, resistance genes and virulence determinants. Our analysis suggests that some of the resistance plasmids that we have identified are circulating in K. pneumoniae strains in Egypt, and are likely a source of antibiotic resistance throughout the world.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; antibiotic resistance; virulence; whole genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae strains isolated in 2012-2016 that differ by antibiotic resistance genes and virulence genes profiles.Pathog Glob Health. 2018 May;112(3):142-151. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2018.1460949. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Pathog Glob Health. 2018. PMID: 29708041 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Genome Sequencing of Extended Spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Hospitalized Patients in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 18;9(1):6266. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42672-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31000772 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens in three tertiary hospitals in Cairo, Egypt.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020 May;39(5):987-992. doi: 10.1007/s10096-020-03812-z. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31953591 Free PMC article.
-
The Animal-foods-environment interface of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Germany: an observational study on pathogenicity, resistance development and the current situation.Vet Res. 2021 Feb 8;52(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00875-w. Vet Res. 2021. PMID: 33557913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae.Open Med (Wars). 2023 May 12;18(1):20230707. doi: 10.1515/med-2023-0707. eCollection 2023. Open Med (Wars). 2023. PMID: 37197355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Epidemiological Analysis of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae Outbreak in a Neonatal Clinic in Poland.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Dec 28;12(1):50. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010050. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36671251 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial for the Special Issue "Antimicrobial Resistance and Genetic Elements in Bacteria".Microorganisms. 2023 Mar 6;11(3):670. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030670. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 36985240 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and comprehensive genome analysis of novel bacteriophage, vB_Kpn_ZCKp20p, with lytic and anti-biofilm potential against clinical multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jan 23;13:1077995. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1077995. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36756618 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenomics analysis of high-risk clone ST147 multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from a patient in Egypt.BMC Microbiol. 2024 Jul 10;24(1):256. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03389-z. BMC Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38987681 Free PMC article.
-
Virulence factors in carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 30;14:1325077. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1325077. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38098668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
- BB/R017689/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- N/A/Egyptian Ministry of Higher Education (Cultural Affairs and Missions Sector) and the Grant Office from the Medical School, Assiut University
- N/A/Deputyship for Research and Innovation, Ministry of Education in Saudi Arabia
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

