Preliminary Evaluation of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extracted Dabai Pulp Oleoresin as a New Alternative Fat
- PMID: 34577016
- PMCID: PMC8470883
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26185545
Preliminary Evaluation of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extracted Dabai Pulp Oleoresin as a New Alternative Fat
Abstract
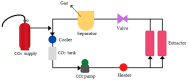
There has been growing interest among food scientists in producing a toxin-free fat as an end product with varying physical or nutritional properties of interest to the food industry. Oleoresin is a rich source of bioactive compounds which consumers can easily add to a large variety of food. Dabai (Canarium odontophyllum) pulp oleoresin (DPL) was extracted using supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) extraction, a green extraction technology. This study investigates the quality of SC-CO2 extracted DPL in discovering its potential as a new alternative fat. The extraction experiment was carried out at a pressure of 40 MPa and a temperature of 40 °C. DPL is a saturated fatty acid (SFA)-rich fat due to its high SFA composition (47.72 ± 0.01%). In addition, the low content of peroxide value (PV) (5.60 ± 0.09 mEq/kg) and free fatty acids (FFA) (3.40 ± 0.03%) indicate the quality and stability of DPL for various applications besides food consumption. DPL also has a low slip melting point (SMP) (20.20 ± 0.03 °C), and HPLC-FID revealed that DPL contained 0.13 ± 0.02 mg/100 g of vitamin E (α-tocopherol), indicating its potential application as a solid fat with a bioactive compound. This present work demonstrates the possible prospect of DPL in the formulation of end products for food industries.
Keywords: alternative fat; oleoresin; quality parameters; supercritical carbon dioxide extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Azlan A., Prasad K.N., Khoo H.E., Abdul-Aziz N., Mohamad A., Ismail A., Amom Z. Comparison of Fatty Acids, Vitamin E and Physicochemical Properties of Canarium Odontophyllum Miq. (Dabai), Olive and Palm Oils. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2010;23:772–776. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2010.03.026. - DOI
-
- Azrina A., Nurul Nadiah M.N., Amin I. Antioxidant Properties of Methanolic Extract of Canarium Odontophyllum Fruit. Int. Food Res. J. 2010;17:319–326. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2010.03.026. - DOI
-
- Khoo H.E., Azlan A., Ismail A., Abas F. Influence of Different Extraction Media on Phenolic Contents and Antioxidant Capacity of Defatted Dabai (Canarium Odontophyllum) Fruit. Food Anal. Methods. 2012;5:339–350. doi: 10.1007/s12161-011-9250-0. - DOI
-
- Kadir N.A.A.A., Azlan A., Abas F., Ismail I.S. Beneficial Effect of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extracted (SC-CO2) Dabai (Canarium Odontophyllum) Pulp Oil in Hypercholesterolemia-Induced SPF Sprague-Dawley Rats. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018;13:1583–1586. doi: 10.1177/1934578X1801301205. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources