Sialyltransferase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer Metastasis: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 34577144
- PMCID: PMC8470674
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26185673
Sialyltransferase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer Metastasis: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
Abstract
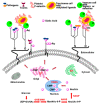
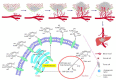
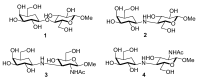
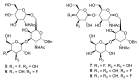
Potent, cell-permeable, and subtype-selective sialyltransferase inhibitors represent an attractive family of substances that can potentially be used for the clinical treatment of cancer metastasis. These substances operate by specifically inhibiting sialyltransferase-mediated hypersialylation of cell surface glycoproteins or glycolipids, which then blocks the sialic acid recognition pathway and leads to deterioration of cell motility and invasion. A vast amount of evidence for the in vitro and in vivo effects of sialyltransferase inhibition or knockdown on tumor progression and tumor cell metastasis or colonization has been accumulated over the past decades. In this regard, this review comprehensively discusses the results of studies that have led to the recent discovery and development of sialyltransferase inhibitors, their potential biomedical applications in the treatment of cancer metastasis, and their current limitations and future opportunities.
Keywords: cancer metastasis; drug design and development; hypersialylation; sialyltransferase; sialyltransferase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of a Novel, Potent, and Selective Sialyltransferase Inhibitor for Suppressing Cancer Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 12;25(8):4283. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084283. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673867 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing the bishomolithocholic acid scaffold for selective sialyltransferase inhibition: A targeted approach to suppress breast cancer metastasis.Eur J Med Chem. 2025 Aug 5;292:117674. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2025.117674. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Eur J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40324300
-
Sialyltransferase inhibition and recent advances.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1864(1):143-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2015.07.007. Epub 2015 Jul 18. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26192491 Review.
-
A novel sialyltransferase inhibitor AL10 suppresses invasion and metastasis of lung cancer cells by inhibiting integrin-mediated signaling.J Cell Physiol. 2010 May;223(2):492-9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22068. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20112294
-
Recent advances in the development of sialyltransferase inhibitors to control cancer metastasis: A comprehensive review.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Sep;165:115091. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115091. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37421784 Review.
Cited by
-
The prognostic value of sialylation-related long non-coding RNAs in lung adenocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 17;14(1):8879. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59130-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38632255 Free PMC article.
-
Anticancer approach by targeted activation of a global inhibitor of sialyltransferases with acrolein.Chem Sci. 2024 May 24;15(25):9566-9573. doi: 10.1039/d4sc00969j. eCollection 2024 Jun 26. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 38939146 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Novel, Potent, and Selective Sialyltransferase Inhibitor for Suppressing Cancer Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 12;25(8):4283. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084283. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673867 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of Sialylation with Decrease in Polysialic Acid Levels Counteracts Transforming Growth Factor β1-Induced Skin Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Transition.Cells. 2024 Jun 19;13(12):1067. doi: 10.3390/cells13121067. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38920695 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic and Therapeutic Implications of Protein and Lipid Sialylation in Human Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 7;25(22):11962. doi: 10.3390/ijms252211962. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596031 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Casimiro S., Luis I., Fernandes A., Pires R., Pinto A., Gouveia A.G., Francisco A.F., Portela J., Correia L., Costa L. Analysis of a bone metastasis gene expression signature in patients with bone metastasis from solid tumors. Clin. Exp. Metastasis. 2012;29:155–164. doi: 10.1007/s10585-011-9438-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shaikhibrahim Z., Lindstrot A., Langer B., Buettner R., Wernert N. Comprehensive gene expression microarray analysis of Ets-1 blockade in PC3 prostate cancer cells and correlations with prostate cancer tissues: Insights into genes involved in the metastatic cascade. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011;27:811–819. - PubMed
-
- Gerlinger M., Rowan A.J., Horswell S., Larkin J., Endesfelder D., Gronroos E., Martinez P., Matthews N., Stewart A., Tarpey P., et al. Intratumor Heterogeneity and Branched Evolution Revealed by Multiregion Sequencing. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012;366:883–892. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1113205. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

