Polyphenols from Citrus Tacle® Extract Endowed with HMGCR Inhibitory Activity: An Antihypercholesterolemia Natural Remedy
- PMID: 34577189
- PMCID: PMC8470345
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26185718
Polyphenols from Citrus Tacle® Extract Endowed with HMGCR Inhibitory Activity: An Antihypercholesterolemia Natural Remedy
Abstract
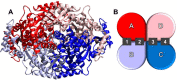
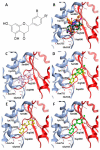
Tacle® is a citrus fruit obtained from the crossbreeding of Clementine and Tarocco cultivars. This fruit retains a promising nutraceutical potential most likely due to a high content in polyphenols, among which the main constituents are the two glycosides naringin and hesperidin. Herein, we evaluated, through an in vitro assay, the capability of Tacle extracts to inhibit the hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase enzyme, which plays a key role in cholesterol biosynthesis. The results obtained spurred us to investigate whether the anti-enzymatic activity observed may be due to a direct interaction of aglycones naringenin and hesperetin with the enzyme catalytic site. Molecular docking simulations indicated that these two compounds are able to anchor to the protein with binding modes and affinities similar to those found for statins, which represent mainstream medications against hypercholesterolemia. The overall results showed an interesting nutraceutical potential of Tacle, suggesting that its extract could be used for dietary supplementation in the treatment of moderate hypercholesterolemia.
Keywords: anti-enzymatic assays; flavanones; molecular docking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Statin-like principles of bergamot fruit (Citrus bergamia): isolation of 3-hydroxymethylglutaryl flavonoid glycosides.J Nat Prod. 2009 Jul;72(7):1352-4. doi: 10.1021/np900096w. J Nat Prod. 2009. PMID: 19572741
-
On the inhibitor effects of bergamot juice flavonoids binding to the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase (HMGR) enzyme.J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Oct 13;58(19):10768-73. doi: 10.1021/jf102576j. J Agric Food Chem. 2010. PMID: 20843083
-
Hydrolysis of flavanone glycosides by β-glucosidase from Pyrococcus furiosus and its application to the production of flavanone aglycones from citrus extracts.J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Nov 27;61(47):11532-40. doi: 10.1021/jf403332e. Epub 2013 Nov 14. J Agric Food Chem. 2013. PMID: 24188428
-
Flavanones: Citrus phytochemical with health-promoting properties.Biofactors. 2017 Jul 8;43(4):495-506. doi: 10.1002/biof.1363. Epub 2017 May 12. Biofactors. 2017. PMID: 28497905 Review.
-
Citrus Flavonoids as Promising Phytochemicals Targeting Diabetes and Related Complications: A Systematic Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 23;12(10):2907. doi: 10.3390/nu12102907. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32977511 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Targeting of mitochondrial fission through natural flavanones elicits anti-myeloma activity.J Transl Med. 2024 Feb 27;22(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05013-0. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38413989 Free PMC article.
-
Metataxonomics and Metabolomics Profiles in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Patients on a "Navelina" Orange-Enriched Diet.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 18;16(20):3543. doi: 10.3390/nu16203543. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39458536 Free PMC article.
-
Nutraceuticals: Focus on Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Cancer, Antioxidant Properties in Gastrointestinal Tract.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jun 28;11(7):1274. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071274. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35883765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Daily Orange Consumption Reduces Hepatic Steatosis Prevalence in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Exploratory Outcomes of a Randomized Clinical Trial.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 20;16(18):3191. doi: 10.3390/nu16183191. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339791 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Cross-Talk Between the Peripheral and Brain Cholesterol Metabolisms.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Feb 11;47(2):115. doi: 10.3390/cimb47020115. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39996836 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

